* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Flow and Cycles of Matter
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
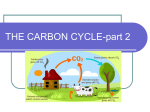
Energy Flow and Cycles of Matter Chapter 53 Energy flow in ecosystems ONE WAY! Laws of thermodynamics always apply: 1. 2. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from 1 form to another Whenever energy is converted from 1 form to another, some of the energy is lost as heat Simplified version: food chain Detailed version: food web Energy input autotroph heterotroph Note that the shows the direction of energy flow Bioaccumulation As substances move through a food chain, some are not passed on These substances can be stored in the bodies of organisms in the food chain – bioaccumulation Fat-soluble toxins tend to build up in higher levels of a food chain – biological magnification Example – DDT pesticide and Bald Eagle Ecological pyramids Used to compare trophic levels Types: Pyramid of numbers Pyramid of biomass Pyramid of energy Ecosystem productivity GPP = gross (total) energy captured during photosynthesis Plants use some of this energy during cellular respiration NPP = net (remaining) energy NPP = GPP – plant respiration Productivity… Influenced by lots of factors: Type of plants Available solar radiation, nutrients, water Maturity of the community Human impacts See table 53-1 p. 1049 Biogeochemical cycles Not one way! Earth is a closed system – matter cannot escape Law of conservation of matter: Matter cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be changed from one form to another. Carbon cycle C is in organic compounds: proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates CO2 is stored in the atmosphere (and in some rocks) Important processes: Photosynthesis Respiration, decomposition, combustion Human impact on carbon cycle – increased combustion has increased amount of CO2 in atmosphere Nitrogen cycle N is found in proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll 78% of atmosphere is N, but this is not in a form that can be absorbed by living things Nitrogen fixation – converts atmospheric N into a form that can be used: combustion, volcanic action, lightning, and nitrogen-fixing bacteria Nitrogen-fixing bacteria – live in nodules on the roots of plants called legumes Nitrogen is returned to the atmosphere during decomposition Phosphorus cycle P is found in nucleic acids, ATP and phospholipids found in cell membranes P is not found as a gas in the atmosphere It cycles from the soil, into the food chain and back Water (hydrologic) cycle Necessary for life: Provides a medium for chemical reactions, transports material throughout bodies, and moderates temperatures Important processes: Precipitation Evaporation, transpiration