* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Monera (Bacteria)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
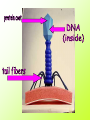
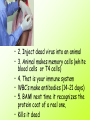
Kingdom Monera (Bacteria) Ciera Verschneider 2009 Characteristics of Bacteria • • • • 1 celled organism (unicellular) Does not have a nuclear membrane Chromosome is a single long chain Lacks organelles like mitochondria or chloroplasts • how big are they? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/conten t/begin/cells/scale/ Shapes • Cocci • Round spheres Bacilli • Rods (pieces of chalk) Spirilli • Corkscrews Movement • Some bacteria have flagella to help them move • Flagella are whiplike tails Reproduction • Fission • One parent cell splits into 2 daughter cells after doubling its DNA • Daughter cells are clones Breathing • Aerobes use oxygen • Anaerobes do not use oxygen Cyanobacteria • Blue green bacteria make food using • Sunlight, CO2, and water due to a colored pigment called • Chlorophyll Good bacteria • • • • • Used to make foods like Cheese Sauerkraut Yogurt And vinegar Saprophyte • Decomposer: breaks down dead materials • (recycles) Nitrogen fixing bacteria • Help farmers to grow plants • (works like fertilizer) Industry uses for • • • • • Make medicine, Enzymes, Cleaners Glues Etc. Bad Bacteria • Pathogen • Bacteria that causes disease • Treat with ANTIBIOTICS • Prevent with VACCINATION Virus • No cells • Only reproduce inside other cells • No form of respiration (energy) Graphic image on next slide Smallpox Reproduction • Attach to outside of host cell • Inject DNA into host, becomes part of host DNA • Copy: host makes copies of virus • Release: host cell bursts, viruses leave to infect new cells Prevent with VACCINE • First vaccine made by Jenner in 1600’s • Used his SON to prevent SMALLPOX To make a vaccine • 1. Kill virus DNA • 2. Inject dead virus into an animal • 3. Animal makes memory cells (white blood cells or T4 cells) • 4. That is your immune system • WBC’s make antibodies (14-21 days) • 5. BAM! next time it recognizes the protein coat of a real one, • Kills it dead Famous Science Dudes • Leeuvenhoek • Microscope 2. Edward Jenner • 1600’s • Made first vaccine to smallpox virus • Tested it on his son 3. Louis Pasteur (1850’s) • • • • • Proved bacteria cause disease Created first rabies vaccine Pasteurization Quickly heat and then cool milk To kill bacteria, but keeps flavor 4. Josef Lister (1850’s) • Germ Theory of Disease • Proved patients would live if doctors and nurses washed their hands in carbolic acid • Hospitals were a place to go to die • They smelled like rotting meat Alexander Fleming (1928) $ went away for vacation, and left some agar plates on the shelf $ came back and noticed no bacteria were growing around a spot of fungus • The fungus was Penicillium notatum, and we now use an extract of the fungus as PENICILLIN (an antibiotic) • Penicillin does not let bacteria form a cell wall 5. Jonas Salk (1940’s) • Polio vaccine