* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
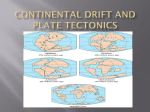
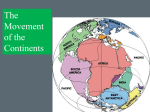
Name:_____________________________________ Period:_____ Date:______________ Chapter 7 The Earth’s Moving Crust Lesson 1 Moving Plates Are the Continents Moving? (p.D6-D7) Movement of Earth’s Crust ________________ are scientists who study Earth and its processes, history, and composition. They can tell that the solid surface, or ______________, of Earth is moving by ________________ its fast and slow movements During _________________ the movement of the Earth’s crust can be seen Geologists also study rocks for signs of ________________________ They can see layers of _______________________________ in rocks that have been twisted or tilted. Motion of Continents In 1912, a German scientist named _______________________, wrote a book called The Origins of Continents and Oceans In his book, he gave evidence that Earth’s ____________________ had once fit together like pieces of a puzzle, forming a single large ___________________ This huge supercontinent was called ________________ meaning “all lands” He proposed the theory of ______________________________ o Stated that Earth’s continents were once joined in a single large landmass that broke apart and the continents _______________ to their current location Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Shapes of the continent’s coastlines _________________ 2. Similar animal and plant ______________ were discovered in places that were far apart a. In matching ________________________ of different continents 3. Age and kinds of ___________ along the edge of one coastline are similar to those on another continent 4. Some __________________________ on different continents seem to match a. As well as ______________ “scars” or marks Wegener did not explain ____________ or __________ the “drifting” took place The continents are NOT ________________ on water; they are part of the Earth’s solid __________________ Studying the _________________ floor might reveal some clues. Q1: How does Wegener’s hypothesis explain why Earth’s surface must be moving? A: ______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Name:_____________________________________ Period: _____ Date:______________ Chapter 7 The Earth’s Moving Crust Lesson 1 Moving Plates Are the Continents Moving? (p.D6-D7) Movement of Earth’s Crust Geologists are scientists who study Earth and its processes, history, and composition. They can tell that the solid surface, or crust, of Earth is moving by observing its fast and slow movements During earthquakes the movement of the Earth’s crust can be seen Geologists also study rocks for signs of movement They can see layers of original horizontality in rocks that have been twisted or tilted. Motion of Continents In 1912, a German scientist named Alfred Wegener, wrote a book called The Origins of Continents and Oceans In his book, he gave evidence that Earth’s continents had once fit together like pieces of a puzzle, forming a single large landmass This huge supercontinent was called Pangea meaning “all lands” He proposed the theory of continental drift o Stated that Earth’s continents were once joined in a single large landmass that broke apart and the continents drifted apart to their current location Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Shapes of the continent’s coastlines match 2. Similar animal and plant fossils were discovered in places that were far apart a. In matching coastlines of different continents 3. Age and kinds of rocks along the edge of one coastline are similar to those on another continent 4. Some mountain ranges on different continents seem to match a. As well as glacier “scars” or marks Wegener did not explain how or why the “drifting” took place The continents are NOT floating on water; they are part of the Earth’s solid crust Studying the ocean floor might reveal some clues. Q: How does Wegener’s hypothesis explain why Earth’s surface must be moving? A: Since different continents match in coastlines, rock type and structure, climate, and ancient and living organisms, then the land masses must have moved from an earlier arrangement.