* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macro Chapter 5
International status and usage of the euro wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Currency War of 2009–11 wikipedia , lookup
Competition (companies) wikipedia , lookup
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Foreign exchange market wikipedia , lookup
Fixed exchange-rate system wikipedia , lookup
Bretton Woods system wikipedia , lookup
Purchasing power parity wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Reserve currency wikipedia , lookup
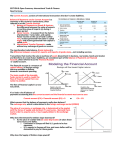
Chapter 5 Presentation 3 Exchange Rates Exchange Rate • The rate at which the currency of one country can be exchanged for the currency of another • http://www.exchangerate.com/ FOREX Market • = FE, FX, Foreign Exchange • Where $ from one nation is exchanged for $ of another • Over $3.2 trillion exchanged daily • Used to convert $ for imports/exports or for speculation • 24 hour market in major financial hubs- New York, Tokyo, London, Franfort FOREX Cont’d • When Americans buy imports, they add dollars to the FOREX market (increase supply) and take foreign currency out of the market • This depreciates the dollar since there are now more dollars supplied in the FOREX • The demand for foreign currency goes up The Foreign Exchange Market Exchange Rates Dollar – Yen Market G 5.1 P Dollar price of 1 yen Sy Exchange Rate: $.01=¥1 .01 Dy Qe Quantity of yen Q Value of the Dollar • Appreciation- the value of the dollar has increased and one can now buy more foreign goods (Imports rise, exports fall) • Depreciation- the international value of the dollar has decreased and it takes more dollars to buy foreign goods (Imports fall, exports rise) Dollar Price • Dollar Price of Pounds is how many dollars it takes to buy one British Pound • When the dollar price goes up (takes more dollars to buy 1 Pound), the dollar has depreciated and the international value of the dollar decreased Trade Restrictions And Help • 1. Tariffs- tax on imported goods • 2. Import quotas- limit on imports • 3. Non-tariff Barriers- difficult requirements and red tape • 4. Export Subsidies- government lowers the production costs which helps to compete with rivals (ex- Airbus received funds from EU countries to compete with Boeing) World Trade Organization (WTO) • 149 nations as members • The WTO oversees international trade agreement and rules on disputes between nations • Pros- increased standard of living • Cons- allows countries to avoid paying high domestic wages Trade Bloc • A group of countries having common identity, economic interests, and trade rules • The nations lower or remove trade restrictions between members to allow free-trade North American Free Trade Agreement (1993) • A major trade bloc between US, Canada, and Mexico • Free trade area between the 3 countries • ***most critics feared that the agreement would allow the US to send jobs to Mexico for low wages • Also would allow South Korea and others to put plants in Mexico and Canada European Union (EU) • Trade bloc of 25 European nations • The Euro is the common currency used by 12 members---GB, Sweden, Denmark all maintained their currency