* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Selectable marker For mammalian cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
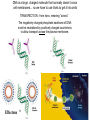
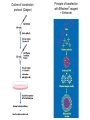
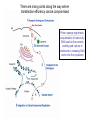
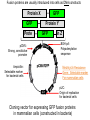
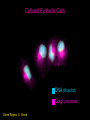
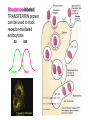
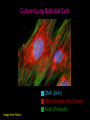
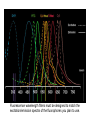
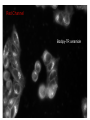
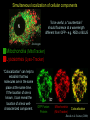
Lab 5A and 5B Overview This Week Last Week Investigating protein sorting signals using cloning, transfection, GFP-fusion proteins, and vital stains for cellular compartments 1. Protein sorting and membrane trafficking - or How cells deliver things to the right place 2. Fluorescent proteins are critical tools in Cell biology 3. Transfection and transgene expression - or How we get DNA into cells to express “designer” genes 4. Fluorescent markers for different compartments of the secretory and endocytic pathways Fusion proteins are usually introduced into cells as DNA constructs Protein X GFP Prote pCMV: Strong, constitutive promoter Ampicillin: Selectable marker for bacterial cells GFP Protein Y GFP in Z BGH pA: Polyadenylation sequence Neomycin: Selectable marker for mammalian cells pUC: Origin of replication for bacterial cells Cloning vector for expressing GFP fusion proteins in mammalian cells (constructed in bacteria) DNA is a large, charged molecule that normally doesn’t cross cell membranes… so we have to use tricks to get it into cells TRANSFECTION - from trans, meaning “across” The negatively-charged phosphate backbone of DNA must be neutralized by positively charged counterions to allow transport across the plasma membrane. Effectene ® Outline of transfection protocol (Qiagen) Principle of transfection with Effectene® reagent + Enhancer There are many points along the way where transfection efficiency can be compromised Proton sponge hypothesis: sequestration of cations by DNA leads to the osmotic swelling and rupture of endosomes, releasing DNA vector into the cytoplasm Only a fraction of treated cells will be successfully transfected, and thus the expression of the transgene will be quite VARIABLE - here GFP is used as a marker of transfection Fusion proteins are usually introduced into cells as DNA constructs Protein X GFP Prote pCMV: Strong, constitutive promoter Ampicillin: Selectable marker for bacterial cells GFP Protein Y GFP in Z BGH pA: Polyadenylation sequence Neomycin Resistance Gene: Selectable marker For mammalian cells pUC: Origin of replication for bacterial cells Cloning vector for expressing GFP fusion proteins in mammalian cells (constructed in bacteria) Alternative strategies to ectopically express genes/siRNAs Electroporation Retroviral Vectors Transfect -High Efficiency -Stable DNA integration -Replication Incompetent -Level 2 Bio-Safety Retrovirus -High Efficiency -Many Cells/even intact tissues -Cell Fusion -Loss of intracellular components Alternative strategies to ectopically express genes/siRNAs Gene Gun -Applicable to many tissues -Penetrates Mitochondria/Chloroplasts -Shallow penetration of particles -Cell damage Microinjection -No selection process -DNA delivery accurately controlled -Minimal perturbation of cells -Technically difficult/few cells 4 transfected constructs U X Y Z 5 vital dye counterstains Golgi Endosome Mitochondria ER Nucleus Ceramide is a LIPID that gets trapped after modification in the Golgi apparatus BODIPY®-TR Ceramide (Molecular Probes) Fluorophore Label Ex Em BODIPYTR Green Red Cultured Epithelial Cells DNA (Hoechst) Golgi (ceramide) Steve Rogers, U. Illinois Iron is carried in blood by the protein TRANSFERRIN and is taken up into cells by endocytosis mediated by the TRANSFERRIN RECEPTOR. Rhodamine-labeled TRANSFERRIN protein can be used to track receptor-mediated endocytosis EX Green EM Red MitoTracker Red CM-H2XRos “…the reduced versions of these probes do not fluoresce EX Green EM Red until they enter an actively respiring cell, where they are oxidized to the fluorescent mitochondrion-selective probe and then sequestered in the mitochondria.” MOLECULAR PROBES handbook Cultured Lung Epithelial Cells DNA (DAPI) Mitochondria (MitoTracker) Actin (Phalloidin) Image from Nikon ER-Tracker Blue-White DPX “ER-Tracker Blue-White DPX is a highly selective and photostable stain for the ER in live cells… Staining at low concentrations does not appear to be toxic to cells.” (MOLECULAR PROBES Handbook) EX UV EM Blue Cultured Endothelial Cells ER (ER-Tracker) Image from Invitrogen 4 transfected constructs U X Y Z 5 vital dye counterstains Golgi Endosome Mitochondria ER Nucleus 20 Data Sets Potential Challenges Encountered in this Week’s Lab Data Management Autofluorescence - increases as cells die Bleed-through between different filter sets Nonspecific labeling of organelles Photobleaching Fluorescence Microscopy Stokes’ shift em intensity ex wavelength excitation and emission filters Fluorophore (or “Fluorochrome”) Excitation maximum Emission maximum Fluorescein 490 520 Rhodamine 550 580 DAPI or Hoechst 345 455 Fluorescence wavelength filters must be designed to match the excitation/emission spectra of the fluorophores you plan to use. Red Channel Bodipy-TR ceramide GFP Channel Autofluorescence of dying cells GFP Simultaneous localization of cellular components To be useful, a “counterstain” should fluoresce at a wavelength different from GFP - e.g. RED or BLUE N -Invitrogen Mitochondria (MitoTracker) Lysosomes (Lyso-Tracker) “Colocalization” can help to establish that two molecules are in the same place at the same time. If the location of one is known, it can reveal the location of a less wellcharacterized component. GFP Fusion Protein Mitochondria (MitoTracker) Colocalization -Beech et al. Science (2000)