* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis II
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
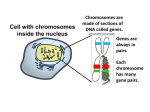
Cells and Heredity Chapter 4 Bell Work 9/30/10 Answer #10-15 on page 95. 4.1 Vocab Sexual reproduction – a cell containing genetic information from the mother and a cell containing genetic information from the father combine into a completely new cell, which becomes the offspring. 4.1 Vocab Cont. Gene – the basic unit of heredity that consists of a segment of DNA on a chromosome Heredity – the passing of genes from parents to offspring Alleles – various forms of a gene. Can be dominant or recessive. Genotype – genes an organism has. Phenotype – the actual characteristics that can be observed Dominant allele – can be observed in the phenotype even if only one copy is present in the genotype Recessive allele – only observed in the phenotype if two copies are Living things inherit traits in patterns. alleles Offspring inherit alleles, which are forms of genes, from their parents. Alleles come on chromosome pairs and can be dominant or recessive. The alleles you have are your genotype; the observable characteristics that come from your genotype are your phenotype. SIMULATION CLASSZONE.COM Try a virtual version of Mendel’s experiment. a gene CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE Bell Work 10/1/10 Please use complete sentences 1. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? 2. Explain why a person with an allele for a particular trait may not have a phenotype that shows the trait. 4.2 Notes Punnett square – illustrates how the parents’ alleles might combine in offspring (ratio, percentage) B = black fur b = brown fur B b BB Bb B b Bb http://www.classzone.com/redirect_science/chm05_pg111_punnett.html bb Homozygous – both traits are the same (both dominant or both recessive) Heterozygous – traits are different (one dominant one recessive) Bell Work 10/7/09 Decide if these statements are true. If not true, correct them. 1. Mitosis produces four genetically identical daughter cells. 2. In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents. 3. Genetic traits are inherited in random patterns. Page 115 #1-6 1. 2. 3. They show how the parents’ alleles may be passed on to offspring Ratios compare one number to another number. A percentage is a ratio that compares a number to 100. Determine all the possible outcomes and represent it as a percentage. Vocab 4.3 Gametes – cells that contain half the usual number of chromosomes. (one chromosome from each pair) 1n cell or haploid cells Egg – a gamete that forms in the reproductive organs of a female. 1n cell or haploid cells Sperm – a gamete that forms in the reproductive organs of a male. 1n cell or haploid cells Fertilization – the process that takes place when a sperm and egg to form one new cell. 2n cell Meiosis Takes place in the reproductive tissues of an organism A single cell goes through two cell divisions (meiosis I and meiosis II) Meiosis I Step 1 - Prophase I Chromosomes condense Duplicated chromosomes pair up with their partners The nuclear membrane disappears Meiosis I Step 2 - Metaphase I Chromosome pairs line up in the middle of the cell Meiosis I Step 3 - Anaphase I Chromosome pairs separate and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell Meiosis I Step 4 - Telophase I and Cytokinesis Nuclear membranes form Cell divides into two daughter cells Meiosis II Step 1 - Prophase II The nuclear membrane disappears Meiosis II Step 2 - Metaphase II Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Meiosis II Step 3 - Anaphase II Chromosomes separate forming individual chromosome and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell Meiosis II Step 4 - Telophase II and Cytokinesis Nuclear membranes form Both cells divide, producing four 1n cells Meiosis is a special form of cell 4.3 division. Meiosis I 1n Meiosis II 1n 1n 1n CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE