* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regulation of gene expression powerpoint
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
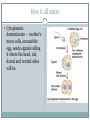
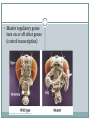
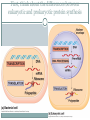
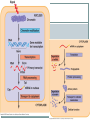
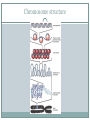
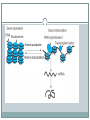
Bellwork What do you think makes cells in the body different from one another; why do lung cells look different than skin cells under a microscope? How do you think this arises? Regulation of gene expression How to get from an egg to a tadpole Cell division – making more cells Cell differentiation – cells become specialized in structure and function Morphogenesis – the process that gives an organism its shape How it all starts Cytoplasmic determinants – mother’s nurse cells, around the egg, sends signals telling it where the head, tail, dorsal and ventral sides will be. Look at pg 372 Inductive signals Induction – changes in the target cells from cells around them What do these signals do? Regulate gene expression!!! Example of a muscle cell Master regulatory genes turn on or off other genes (control transcription) Now, more specifically, how is gene expression controlled? First, think about the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic protein synthesis A lot of mechanisms for gene regulation Prokaryotes (ex. Bacteria) Negative regulation Inducible operons Repressible operons Positive regulation Activator proteins Eukaryotes Regulation at all stages of protein synthesis Chromosome structure Histone acetylation