* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Disorders
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
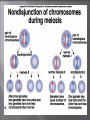
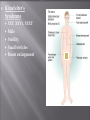
Gene disorder refers to the harmful effect a detrimental allele produces when it occurs at a significant frequency in a population. Most disorders are rare because affected individuals often die at a relatively young age, or cannot reproduce. Not all defects are recessive. For example, Huntingtons disease is autosomal dominant. Human somatic cells normally have 23 pairs of chromosomes. divided into seven groups characterized by size and shape 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes XX = Female XY = Male Failure of chromosomes to separate correctly during meiosis I or II is called primary nondisjunction. Down Syndrome caused by trisomy 21 1 in 1700 for mothers < 20. 1 in 1400 for mothers >20<30. 1 in 750 for mothers >30<35. 1 in 16 for mothers >45. Down Syndrome Chromosome 21 does not separate correctly. They have 47 chromosomes in stead of 46. Children with Down Syndrome develop slower, may have heart and stomach illnesses and vary greatly in their intelligence. X Chromosome XXX or XXY yields Klinefelter syndrome XO yields Turner syndrome Y Chromosome XYY - Jacob syndrome Klinefelter’s Syndrome XXY, XXYY, XXXY Male Sterility Small testicles Breast enlargement Turner’s Syndrome X Female sex organs don't mature at adolescence sterility short stature XYY Syndrome or Jacob Syndrome Normal male traits Often tall and thin Associated with antisocial and behavioral problems Sickle-cell anemia is a recessive inherited disorder in which afflicted individuals have defective hemoglobin, and thus are unable to properly transport oxygen to tissues. Homozygotes have sickle-cell. Heterozygotes usually appear normal, but are resistant to malaria. Cri-du-chat Deletion of material on 5th chromosome Characterized by the cat-like cry made by cridu-chat babies Varied levels of mental handicaps Genetic counseling identifies parents at risk of producing children with genetic defects and assesses the state of early embryos. High-risk pregnancies couples with recessive alleles mothers older than 35 amniocentesis chorionic villi sampling Counselors can look for three things in cell cultures in search of genetic disorders: aneuploidy or gross alterations proper enzyme functioning association with known genetic markers Mutations are accidental changes in genes. •rare, random, and usually result in recessive alleles •pedigrees are used to study heredity • Family pedigrees – Chart of family’s history • Key –Males-squares, females-circles –Shaded means individual is affected by disorder –Line between square and circle indicates a union –Vertical line downward indicates child »Multiple children are drawn off a horizontal line • Pedigrees for autosomal disorders – An affected child from 2 unaffected parents indicates an autosomal recessive trait • Counselor can suggest genetic testing – Two affected parents produce an unaffected child • Indicates both parents are heterozygous for an autosomal dominant trait • Another indicator- when both parents are unaffected, none of their children are either – Study the two pedigrees on the following slides To make a karyotype - Arrange chromosomes in matching pairs from largest to smallest. Gel from gel electrophoresis Inherited condition where blood is slow to clot or does not clot at all only expressed when individual has no copies of the normal allele Royal hemophilia - sex-linked • Pedigrees for sex-linked disorders – X-linked disorders • X-linked recessive disorders –To be affected, daughters must inherit it from both parents –Sons can only inherit it from mother, therefore more males affected than females • X-linked dominant disorders –Affected males pass the trait only to daughters –Females can pass trait to both daughters and sons – Y-linked disorders • Present only in males • Fathers pass trait to all sons – Study the pedigree on the following slide The human genome project Goals To construct a base sequence map To construct a genetic map of each chromosome The base sequence map Humans share many genes in common with all other living organisms The genetic map Researchers only need to know a short sequence of bases in a gene, and a computer searches the genome for a match Is it right to use cloning to create an entirely new human being? Is it ethical to create an embryonic copy of John Doe to supply cells to keep John alive? Does a multicellular ball of tissue -- an embryo -- have the same rights and status as a human being?