* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis Chapeter 11 section #4
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
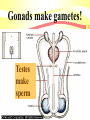
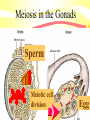
Meiosis & Genetics Sexual Cell Reproduction Ch. 10.2 Genetics The Study of Inherited Characteristics Chromosome DNA Code for traits Genes on chromosomes: • Segments of DNA on a chromosome • Code for a trait Hair Color Eye Color Gene Segment For Hair color Trait • Characteristic • Feature • Variations in a population Chromosome Number •Homologous Different # for different species Chromosomes • Full set = 2N=Diploid are the sets of • N= pair •each # pairs • 1 pair from mother • 1 pair from father • Humans= 23 pairs or • 46 total Autosomes & Sex Chromosomes Autosomes = # 122 for all traits except sex Sex chromosomes= Pair # 23 XX(female) or XY(male) Why do cells divide by Meiosis? Sperm • To reduce chromosome number • In sex cells • Or in single celled organisms: • Under changing conditions for • Chromosome Variety N egg N 2N baby Gonads make gametes! Testes make sperm Gonads make gametes! Ovaries make eggs Gamete develoment 2N 1N • Imature egg or sperm cell = full set of chromosome (2N) • Undergoes meiosis with 2 cell divisions • Develops into a mature egg or sperm (1N) Meiosis in the Gonads Sperm Meiotic cell division Egg Stages in Meiosis: • Interphase • • • • • • • • Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Final Telophase • Full set of chromosomes (2N) • DNA has doubled (4N) • 1st cell division (2N) • DNA does not double • 2nd division • Sperm & Egg (1N) Meiotic Cells…….. 2N • Divide twice to • 1/2 Chromosome number • “Haploid” • Sperm or eggs Immature Egg or sperm 4N 2N 1N 1N 2N 1N 1N Genetic Recombination • Variety in chromosomes from • Crossing over = • Exchange of parts • Of Homologous chromosomes A B B A Nondysjunction = chromosomes fail to “dis-join” or separate: • Trisomy=gamete with 3 of one type • Monosomy=gamete with 1 of one type • Tripoidy= zygote with three of one type 2N egg 2N 2N Eggs forming 2nd division 2N empty + 1N sperm 1N 1N = 3N Down Syndrome= 3 of #21 Klinefelter’s = XXY Turner’s Syndrome • XO sex chromosome • Instead of XX female • Or XY for male: X + Empty sperm = XO