* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disorders review - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
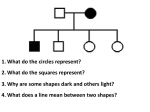
Chapter 14 Review Human Genetic Disorders This organized picture of an individual’s chromosomes is called karyotype a __________________ The person in this picture is a male female Female There are 2 X and no y chromosomes. The genetic disorder in which the person can’t make the protein needed to make their blood clot is called hemophilia ______________________ Name an X-linked genetic disorder. Hemophilia, colorblindness, Duchenne Muscular dystrophy A person who has a copy of the gene for a recessive disorder but doesn’t show any signs of the sickness carrier is called a _________________ A person with trisomy-21 Down syndrome (three #21 chromosomes) has ____________ Genetic disorder in which a person can NOT breakdown phenylalanine and eating foods containing this amino acid causes them to become retarded. Phenylketonuria (PKU) TRUE or FALSE Males can NOT be carriers for autosomal recessive disorders. False. Males CAN carry AUTOSOMAL disorders, they just can’t be carriers for X linked disorders. The cell that forms when an egg and a sperm zygote join together is called a _______________ TRUE or FALSE GERM cell mutations can be passed on to offspring. TRUE : Germ cells are reproductive cells. Changes in the DNA of these cells is passed on to the offspring. Genetic disorder in which the DNA code for hemoglobin is changed. Red blood cells with the damaged hemoglobin protein, change into a sickle shape and clog up the blood vessels. Sickle cell anemia TRUE or FALSE An autosomal trait is found on the X chromosome FALSE Autosomes are the chromosomes that are NOT sex chromosomes. A trait that is controlled by several genes (like skin color or height) is called ______________ Polygenic Give an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disease. Huntington’s ; Achondroplasia (dwarfism) A trait in which there are three or more choices for a single gene (like A, B, and O blood type) is a Multiple allele trait. ____________ polygenic multiple allele Give an example of Y linked gene. Hairy ears (pinna) TRUE or FALSE Dizygotic or fraternal twins have identical DNA False They come from 2 different eggs and 2 different sperm Eye color is a _____________ trait. Polygenic polygenic Multiple allele sex linked A body cell is also called a ______________ SOMATIC cell. LETHAL ______________ mutations cause death often before birth. A person with the Xy genotype would be male female male GERM cell mutation happens in A _________ sperm or egg cells. Twins which don’t separate entirely and remain attached by some body part are called ______________ Conjoined A C B Which person shows the genetic trait? A Twins that come from one sperm and egg Maternal or are called _____________ MONOZYGOTIC A C B D Which person is a carrier for the trait? C This picture shows pedigree a ___________________ Karyotype Pedigree Punnett square Show up more frequently in males X-linked genes _______________ A. Only show up in females B. Show up more frequently in males C. can be heterozygous in males D. only pass from mothers to daughters TRUE or FALSE MONOZYGOTIC (or maternal) TWINS have identical DNA. TRUE Name the disease that individual’s who are heterozygous for the sickle cell allele show resistance to. malaria Sickle cell anemia is more common in ____________________ Males females African Americans Caucasians African Americans Cystic fibrosis is more common in ___________ Males females Caucasians African Americans Caucasians A gene that is carried on the X chromosome X-linked A trait with 3 or more choices for a gene (like A B and O blood type alleles) Multiple allele trait Twins with different DNA that come from 2 different egg and sperm are called dizygotic or Fraternal TRUE or FALSE Sex linked genes are found on the X or y chromosome. True; sex LINKED means they are on one of the sex chromosomes. Dark spot in the nucleus made when one of the X chromosomes in females is inactivated BARR BODY When homologous chromosomes don’t separate nondisjunction during meiosis it is called _________________ Which type of mutation can be passed along to offspring? Somatic cell mutation Germ cell mutation Germ cell mutation Which of the following is NOT visible in a karyotype ? Sex of baby Missing or extra chromosomes a point mutation Point mutations Name 3 disorders that are: Autosomal recessive _______________(PKU) Phenylketonuria Tay-Sach’s ________________ Cystic fibrosis ________________ X linked recessive _______________ Hemophilia Colorblindness _______________ Muscular dystrophy _______________ Name 3 disorders that is caused by nondisjunction: ___________________ Down syndrome ___________________ Turner’s syndrome ___________________ Klinefelter’s syndrome Name disorders that are: Autosomal Dominant ________________ Huntington’s ________________ Achondroplasia Autosomal Codominant ___________________ Sickle cell disease Which parent determines the sex of the baby? father What is the difference between a germ cell mutation and a somatic cell mutation? Somatic cells are body cells and mutations in these cells are NOT passed on to offspring. Germ cells are reproductive cells. Mutations in these cells CAN be passed on to offspring. Twins with identical DNA that come from the same egg and sperm are called Monozygotic or Maternal Chromosomes that DON’T determine sex are autosomes called ____________________ Other name for “Dwarfism” Achondroplasia TRUE or FALSE Females can be carriers for X linked genes. True; they have 2 X chromosomes. So they can have one normal gene and one mutant gene. The cell that forms when an egg and a sperm zygote join together is called a _______________ TRUE or FALSE Somatic cell mutations can be passed on to offspring. False; they are in body cells. They can make the cell unable to function; cause cancer; or kill the body cell BUT are NOT PASSED ON TO OFFSPRING. TRUE or FALSE Females can be carriers for X linked genes TRUE Why do X-linked recessive disorders show up more in males than females? Males only have one X. If they get the gene it will show. Females have a 2nd X that can “hide” the disorder gene. They need 2 copies of the gene to show disorder. Males don’t have a “back up” X. What disorder is it? Mutation in the blood clotting protein makes Hemophilia person unable to stop bleeding after an injury _______________ Mutation in hemoglobin causes red blood Sickle cell anemia cells to change shape and ____________________ clog up blood vessels Phenylketonuria (PKU) Mutation causes mental retardation if foods containing phenylalanine are eaten _____________________ Three #21 chromosomes are present causing mental retardation Down syndrome _______________________ Mutation in ion channel protein causes thick mucous to clog up lungs and Cystic fibrosis digestive organs _______________________ What disorder is it? Gradual deterioration of the brain that appears during middle age resulting in nursing home care and early death Huntington’s ____________________ disease (HD) Progressive weakening of muscle proteins resulting in inability to walk Duchenne Muscular dystrophy and eventually death _________________________ Inability to distinguish between the colors red and green _____________________ Colorblindness Only one X and no y chromosome resulting in infertility Turner syndrome ____________________ What disorder is it? Conjoined twins Twins that are born joined together ____________________ Klinefelter syndrome Males with an extra X chromosome ______________________ (XXY) karyotype; some female features; infertility Lipids build up in brain causing Tay-Sachs blindness, retardation, & early death _________________________ achondroplasia Disorder in bone growth so torso __________________________ and head are normal size but arms and legs are short Dominant/recessive? Autosomal/X-linked/nondisjunction Turner syndrome Nondisjunction ____________________ Cystic fibrosis ____________________ Autosomal recessive Hemophilia _____________________ X-linked recessive Colorblindness X-linked recessive __________________ Autosomal recessive Phenylketonuria ___________________ X-linked recessive Duchenne muscular dystrophy ________________ Dominant/recessive? Autosomal/X-linked/nondisjunction Phenylketonuria Down syndrome Autosomal recessive ____________________ nondisjunction ____________________ Sickle cell anemia Klinefelter syndrome Autosomal CODOMINANT _____________________ nondisjunction ____________________ Autosomal dominant Huntington’s disease ______________________ Autosomal recessive Tay-Sachs _________________