* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz Show
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
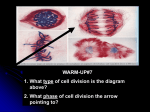
Chapter 11 – Introduction to Genetics Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4 Topic 5 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 FINAL ROUND Topic 1: $100 Question Question: The chemical factors that determine traits are called a. alleles. b. genes. c. characters. d. traits. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $100 Answer Question: The chemical factors that determine traits are called a. alleles. b. genes. c. characters. d. traits. BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $200 Question Question: Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study a. flowering b. cross-pollination c. the inheritance of traits d. gamete formation ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $200 Answer Question: Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study a. flowering. b. cross-pollination. c. the inheritance of traits. d. gamete formation. BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $300 Question Question: When Gregor Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short plants, all the offspring were tall because a. the allele for tall plants is recessive. b. the allele for short plants is dominant. c. the allele for tall plants is dominant. d. they were true-breeding like their parents. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $300 Answer Question: When Gregor Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short plants, all the offspring were tall because a. the allele for tall plants is recessive. b. the allele for short plants is dominant. c. the allele for tall plants is dominant. d. they were true-breeding like their parents. BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $400 Question Question: A tall plant is crossed with a short plant. If the tall F1 pea plants are allowed to self-pollinate, a. The offspring will be of medium height. b. Some of the offspring will be tall, and some will be short. c. All of the offspring will be tall. d. All of the offspring will be short. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $400 Answer Question: A tall plant is crossed with a short plant. If the tall F1 pea plants are allowed to self-pollinate, a. The offspring will be of medium height. b. Some of the offspring will be tall, and some will be short. c. All of the offspring will be tall. d. All of the offspring will be short. BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $500 Question Question: When you flip a coin, what is the probability that it will come up tail? a. 1/2 b. 1/4 c. 49% d. 51% ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 1: $500 Answer Question: When you flip a coin, what is the probability that it will come up tail? a. 1/2 b. 1/4 c. 49% d. 51% BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $100 Question Question: The farther apart two genes are located on a chromosome, the a. less likely they are to be inherited together. b. more likely they are to be linked. c. less likely they are to assort independently. d. less likely they are to be separated by a crossover during meiosis. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $100 Answer Question: The farther apart two genes are located on a chromosome, the a. less likely they are to be inherited together. b. more likely they are to be linked. c. less likely they are to assort independently. d. less likely they are to be separated by a crossover during meiosis. BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $200 Question Question: If two genes are on the same chromosome and rarely assort independently, a. crossing-over never occurs between the genes. b. crossing-over always occurs between the genes. c. The gene are probably located far apart from each other. d. The genes are probably located close to each other. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $200 Answer Question: If two genes are on the same chromosome and rarely assort independently, a. crossing-over never occurs between the genes. b. crossing-over always occurs between the genes. c. The gene are probably located far apart from each other. d. The genes are probably located close to each other. BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $300 Question Question: Gene maps are based on a. The frequencies of crossing-over between genes. b. Independent assortment. c. The number of genes in a cell d. Genetic diversity. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $300 Answer Question: Gene maps are based on a. The frequencies of crossing-over between genes. b. Independent assortment. c. The number of genes in a cell d. Genetic diversity. BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $400 Question Question: Linked genes a. are never separated. b. are always recessive. c. are on the same chromosome. d. assort independently. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $400 Answer Question: Linked genes a. are never separated. b. are always recessive. c. are on the same chromosome. d. assort independently. BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $500 Question Question: Which of the following assort independently? a. codominant alleles b. multiple alleles c. genes on the same chromosome. d. chromosomes. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 2: $500 Answer Question: Which of the following assort independently? a. codominant alleles b. multiple alleles c. genes on the same chromosome d. chromosomes BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $100 Question Question: Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of a. Two genetically identical cells. b. Four genetically identical cells. c. Two genetically different cells. d. Four genetically different cells. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $100 Answer Question: Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of a. Two genetically identical cells. b. Four genetically identical cells. c. Two genetically different cells. d. Four genetically different cells. BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $200 Question Question: Why did Thomas Hunt Morgan use fruit flies in his studies? a. Fruit flies produce a large number of offspring. b. Fruit flies take a long time to produce offspring. c. Fruit flies share certain characteristics with pea plants. ANSWER d. Fruit lies have a long lifespan. BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $200 Answer Question: Why did Thomas Hunt Morgan use fruit flies in his studies? a. Fruit flies produce a large number of offspring. b. Fruit flies take a long time to produce offspring. c. Fruit flies share certain characteristics with pea plants. d. Fruit lies have a long lifespan. BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $300 Question Question: The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol a. Z. b. X. c. N. d. Y. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $300 Answer Question: The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol a. Z. b. X. c. N. d. Y. BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $400 Question Question: A heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a short plant. The probability that an F1 plant will be tall is a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100% ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $400 Answer Question: A heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a short plant. The probability that an F1 plant will be tall is a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100% BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $500 Question Question: Organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to be a. hybrid b. heterozygous c. homozygous d. dominant ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 3: $500 Answer Question: Organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to be a. hybrid b. heterozygous c. homozygous d. dominant BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $100 Question Question: What principle states that during gamete formation genes for different traits separate without influencing each other’s inheritance. a. principle of independent assortment b. principle of dominance c. principle of prohibition d. principle of segregation ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $100 Answer Question: What principle states that during gamete formation genes for different traits separate without influencing each other’s inheritance. a. principle of independent assortment b. principle of dominance c. principle of prohibition d. principle of segregation BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $200 Question Question: Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over another allele for that gene are called a. multiple genes. b. multiple alleles. c. polygenic inheritance. d. incomplete dominance. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $200 Answer Question: Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over another allele for that gene are called a. multiple genes. b. multiple alleles. c. polygenic inheritance. d. incomplete dominance BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $300 Question Question: Gregor Mendel’s principles of genetics apply to a. plants only. b. animals only. c. pea plants only. d. all organisms. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $300 Answer Question: Gregor Mendel’s principles of genetics apply to a. plants only. b. animals only. c. pea plants only. d. all organisms. BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $400 Question Question: If an organism’s diploid number is 12, its haploid number is a. 12 b. 24 c. 3 d. 6 ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $400 Answer Question: If an organism’s diploid number is 12, its haploid number is a. 12 b. 24 c. 3 d. 6 BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $500 Question Question: Gametes have a. one allele for each gene. b. two sets of chromosomes. c. twice the number of chromosomes found in body cells. d. homologous chromosomes. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 4: $500 Answer Question: Gametes have a. one allele for each gene. b. two sets of chromosomes. c. twice the number of chromosomes found in body cells. d. homologous chromosomes. BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $100 Question Question: Gametes are produced by the process of a. mitosis b. meiosis c. replication d. duplication ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $100 Answer Question: Gametes are produced by the process of a. mitosis b. meiosis c. replication d. duplication BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $200 Question Question: Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of a. diploid cells. b. 2N daughter cells. c. haploid cells. d. body cells. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $200 Answer Question: Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of a. diploid cells. b. 2N daughter cells. c. haploid cells. d. body cells. BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $300 Question Question: What is being shown in the figure? a. independent assortment b. replication c. crossing-over d. metaphase I of meiosis ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $300 Answer Question: What is being shown in the figure? a. independent assortment b. replication c. crossing-over d. metaphase I of meiosis BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $400 Question Question: Chromosomes form tetrads during a. anaphase II of meiosis. b. telophase I of meiosis. c. prophase I of meiosis. d. metaphase I of meiosis. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $400 Answer Question: Chromosomes form tetrads during a. anaphase II of meiosis. b. telophase I of meiosis. c. prophase I of meiosis. d. metaphase I of meiosis. BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $500 Question Question: What happens between meiosis I and meiosis II that reduces the number of chromosomes? a. replication occurs twice. b. replication does not occur. c. crossing-over. d. Metaphase occurs. ANSWER BACK TO GAME Topic 5: $500 Answer Question: What happens between meiosis I and meiosis II that reduces the number of chromosomes? a. replication occurs twice. b. replication does not occur. c. crossing-over. d. Metaphase occurs. BACK TO GAME FINAL ROUND Question Question: a. Choice 1 b. Choice 2 c. Choice 3 d. Choice 4 ANSWER BACK TO GAME FINAL ROUND Answer Question: a. Choice 1 b. Choice 2 c. Choice 3 (correct answer) d. Choice 4 BACK TO GAME