* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Disorders
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
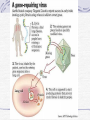
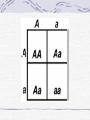
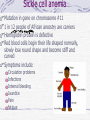
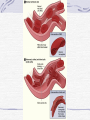
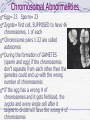
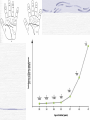
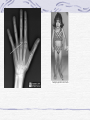
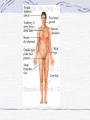
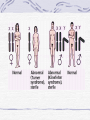
Genetic Disorders Genetic Disorders Can be from changes in base sequence of DNA Can also be chromosomal abnormalities: Missing a whole chromosome An extra chromosome Missing fragment of chromosome Mutations Change in the “normal” base sequence in DNA Leads to change in the sequence of amino acids in a protein Most genetic disorders are caused by this Cystic fibrosis Most common genetic disorder in caucasians of western european descent A recessive mutation on chromosome #7, missing three bases of DNA 1 in 3200 births= rr 10 million carriers in the U.S. (Rr) Defective protein in cell membrane causes a thick mucus to clog lungs, pancreas, digestive tract, reproductive tract Chronic (reoccuring) lung infections, digestion problems Phenylketonuria A mutation that is a recessive allele on chromosome # 12 1 in 50 people is a carrier 1 in 10,000 babies born with it A defective enzyme that is supposed to convert the amino acid phenylalanine in to tyrosine If they eat foods with phenylalanine, it accumulates in brain cells, causes them to die Causes mental retardation Can’t eat foods high in protein, because proteins are made of amino acids, including phenylalanine Sickle cell anemia Mutation in gene on chromosome #11 1 in 12 people of African ancestry are carriers Hemoglobin protein is defective Red blood cells begin their life shaped normally, slowly lose round shape and become stiff and curved Symptoms include: Circulation problems Infections Internal bleeding Jaundice Pain fatigue Sickle cell, cont. Treatments: Transfusion Vitamins Pain medication Average life span: 42-48 years Chromosomal Abnormalities Egg= 23 Sperm= 23 Zygote= first cell, SUPPOSED to have 46 chromosomes, 1 of each Chromosome pairs 1-22 are called autosomes During the formation of GAMETES (sperm and egg) if the chromosomes don’t separate from each other then the gametes could end up with the wrong number of chromosomes If the egg has a wrong # of chromosomes and it gets fertilized, the zygote and every single cell after it begins to divide will have the wrong # of chromosomes Most of the time, if the zygote has the wrong number of chromosomes then it will not divide, and it will die before the woman even knows she was pregnant. There are a FEW EXCEPTIONS: Down’s Syndrome (Trisomy 21) During the formation of an egg or sperm, chromosome pair #21 didn’t separate= a gamete had an extra #21 chromosome Person’s genotype is 47(21) Symptoms of Down’s Syndrome HUGE variation among individuals Mild to severe mental retardation Almond shaped eyes Shorter limbs, stature Poor muscle tone Large space between first and second toe Large, protruding tongue Heart defects Gastroesophageal reflux disease Thyroid problems Prenatal Testing Women are offered a test called the AFP test (alpha feto protein test) at 1618 weeks of gestation Elevated level of certain proteins in mother’s blood stream can be an indicator of a baby with down’s syndrome Turner’s Syndrome Person is X0 for genotype of sex chromosomes (45, X0) Lacking a y chromosome makes the person a female Symptoms Short stature Swelling of hands/feet Broad chest Low hairline Low-set ears Sterile *rudimentary ovaries *obesity *short metacarpal IV *webbed neck *poor breast development *heart problems Kleinfelter’s Syndrome Person’s genotype is XXY (47,XXY) Male (because of presence of y chromosome) 1 in 500 males Symptoms include: Hypogonadism- produces little or no hormones Breast enlargement Little facial hair, body hair Narrow shoulders Harlequin Type Ichthyosis Characterized by a thickening of the • keratin layer in fetal human skin. • In addition , the eyes, ears , mouth and other appendages may be abnormally contracted. Primordial Dwarfism Dwarfism: Achondroplasia