* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LEQ: What did Mendel discover about the patterns of inheritance?
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
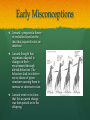
LEQ: What did Mendel discover about the passing on of traits? 9.1 to 9.3 Early Misconceptions Lemark – proposed a theory of evolution based on the idea that acquired traits are inherited Lamark thought that organisms adapted to changes in their environment through altered behaviors. The behaviors lead to selective use or disuse of given structures causing them to increase or decrease in size. Lamark went on to claim that this acquired change was then passed on to the offspring. Early Misconceptions Blended Inheritance – the traits of parents blend in the offspring Gregor Mendel Father of Genetics – deduced the fundamental principles of inheritance Published in 1866 – not recognized as important until long after his death <iframe width="560" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/_pb1Pq5PCsU" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> Pea Plant Experiments Mendel used pea plants for his heredity experiments because… Controlled breeding Cheap Easy to grow and maintain Grow many in a small space Quick generation time 7 contrasting traits Fertilization in Pea Plants Self-fertilization Pollen of one plant fertilizes the egg of the same plant Cross-fertilization Pollen of one plant fertilizes the egg of a second plant True-breeding vs. Hybrid True-breeding Organisms that when selfpollinated (or crossed with one of the same) produce an organism identical to self Hybrid Offspring produced from crossing 2 dissimilar organisms Generations P – Parent Generation; the original cross F1 – First Filial Generation; Offspring of the parent cross F2 – Second Filial Generation; Offspring of the F1 generation Seven Characteristics Monohybrid Crosses Genetic cross of individuals differing in one trait Trait – a characteristic that is inherited from parent to offspring; controlled by a gene Examples: flower color, plant height, etc… Punnett Square – diagram used to predict the possible outcome of a given cross Vocab… Allele – different forms of a gene Example: flower color could be white or purple; plant height could be tall or short Homozygous alleles are the same Heterozygous alleles are different Dominant Allele that is expressed when it is present; represented using capitol letters Recessive Allele that is only expressed in the absence of the dominant allele; represented using lower case of dominant letter Phenotype Physical appearance Genotype Genetic Make-up (the letters) Mendel’s Experiment Mendel’s Law of Segregation A sperm or egg carries only 1 allele for each inherited trait because allele pairs separate from each other during the production of gametes When does segregation occur? Anaphase I of meiosis when homologous chromosomes are separated. LEQ: How are Punnett Squares used to predict the outcomes of a cross? 4 boxes Define parents Define alleles A = normal pigment a = albino Possible alleles from one parent across the top Aa X Aa A or a Possible alleles from 2nd parent along the side A or a Fill in boxes bring letters down and across Give genotype and phenotype ratios 1 AA: 2Aa: 1aa 3 normal: 1 albino