* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12 Review & Wrap-up
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
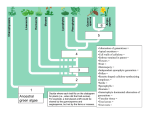
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 12 Review & Wrap-up 1. What is a pedigree? 1. Graphical representation of a families genetic inheritance. 2. What is a pedigree used for? 2. Help determine the likelihood of given trait to show up in the offspring. 3. What does a square stand for? Circle? 3. Male Female 4. What is indicated by a shaded shape? 4. The individual is affected. 5. What is a carrier? 5. An individual who is heterozygous for a given trait but does not show the trait. 6. A recessive trait which causes an accumulation of thick mucus in the lungs and digestive tract. 6. Cystic Fibrosis 7. The absence of an enzyme that breaks down a lipid produced in the central nervous system(brain). 7. Tay-sachs disease 8. A lethal genetic disorder caused by a dominant allele. 8. Huntington’s disease 9. If Huntington’s disease is lethal, how is it passed on? 9. It does not affect an individual with the disorder until they are between the ages of 30-50. 10. In this type of inheritance, the phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate to those of the two homozygotes. 10. Incomplete dominance 11. This type of trait is controlled by more than two alleles. Give an example. 11. Multiple alleles ABO blood group 12. This trait is controlled by two or more genes. Give an example. 12. Polygenic inheritance skin color, eye color, height 13. What is the difference between the sex and autosomal chromosomes. 13. Sex chromosomes determine the sex of an individual. The rest of an individuals chromosomes are autosomal. 14. In this type of inheritance, the phenotype of both homozygotes is produced in a heterozygote individual. 14. Codominance 15. List some examples of environmental factors that can affect gene expression. 15. Temperature, nutrition, light, chemicals, infectious agents, hormone levels, age. 16. What happens as a result of hemophilia? 16. Blood is not able to clot due to the shape of the cells, affected individuals can bleed to death due to simple wounds. 17. What is a sex linked trait? Give an example. 17. Sex linked traits are carried on a sex chromosome red-green color blindness and hemophilia. 18. Why is it that a male is more likely to receive a recessive sex-linked trait (found on X chromosome) that a female? 18. Males only receive one X chromosome…if it carries the disorder they will show that trait. 19. What do we use a karyotype for? 19. To detect genetic disorders in an individual.