* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Disorders, Disease, and Karyotypes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
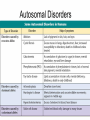
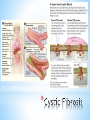
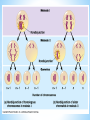
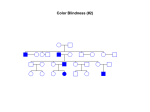
* 14.1 and 14.2 * Disease determined by inheritance of an allele * There are three possibilities for genetic disease: * Recessive: disorder caused by having 2 recessive alleles * Dominant: disorder caused by having at least one copy of the dominant allele * Co-dominant: heterozygous genotype gives a different phenotype * *A.Cystic fibrosis: Homozygous recessives (cc) have cystic fibrosis - body cannot make needed chloride channel, high concentrations of extracellular chloride causes mucous to build up, infections, pneumonia. Diet, antibiotics and treatment can extend life to 25 years or more. *B.Tay-Sachs: Enzyme that breaks down brain lipids is non-functional in homozygous recessives (tt). Buildup of lipids causes death by age 2-3 * * *Achondroplasia (dwarfism): AA = Homozygous dominant is lethal – usually fatal before or shortly after birth. Aa = dwarfism. aa = no dwarfism. 99.96% of all people in the world are homozygous recessive (aa) *Sporadic mutation can occur from paternal gene during spermatogenesis and then be passed on * * *Polydactyly (extra fingers or toes): PP or Pp = extra digits, pp = 5 digits. 98% of all people in the world are homozygous recessive (pp) * Manifests in many ways including: -a small extra bump on the side of the hand, -a finger which widens to end in two fingertips, -an extra finger which dangles by a thin cord from the hand -a hand which looks normal except that it has a thumb and five fingers * *Sickle Cell Anemia * SS= sickle cell anemia (misshapen Sickle Cell: many believe sickle cell anemia co evolved with malaria cells lead to death) life expectancy approx: 43 yrs * AA= normal red cells, healthy * AS= not enough sickle cells to kill and resistant to malaria! (body destroys the sickle cells and the parasite) * *Mistakes can happen in Meiosis *Most common = Non-Disjunction *Results in wrong chromosome number in gametes *Examples include: *Trisomy 21 (Down’s Syndrome) with an extra # 21 *Klinefelter’s Syndrome (XXY) * *During puberty, the physical traits of the syndrome become more evident; because these boys do not produce as much testosterone as other boys, they have a less muscular body, less facial and body hair, and broader hips. As teens, XXY males may develop breast tissue and also have weaker bones, and a lower energy level than other males. *Occurs in 1/500 to 1/1000 live births * *Humans have 46 chromosomes *Occurs in 23 pairs (most autosomes) *2 of the 46 are sex-determining chromosomes (X and Y) *XX=Female, XY=Male *Picture of chromosomes=karyotype *Doctors use to determine sex of baby and genetic abnormalities * * *