* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B1 Revision - Rougemont School
Survey
Document related concepts
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
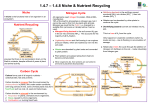
Environment – Answer the Following • Outline intensive farming methods that can be used to increase yields from plants. B1 Environment – Answer the Following • Outline intensive farming methods that can be used to increase yields from plants. 1. Fertilisers – more plant growth 2. Pesticides – kill pests which would eat crops 3. Disease control – prevents loss of crop from disease Environment – Answer the Following • Outline intensive farming methods that can be used to increase yields from animals. B1 Environment – Answer the Following • Outline intensive farming methods that can be used to increase yields from animals. 1. 2. 3. 4. Disease control – prevents loss of animals to disease Battery methods – reduced space for animals So animals use less energy So less food needed Environment – Answer the Following • Describe how untreated sewage and fertilisers may ultimately cause fish to die. B1 Environment – Answer the Following • Describe how untreated sewage and fertilisers may ultimately cause fish to die. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Fertilisers/sewage encourage rapid growth of plants Deeper plants die due to lack of light Microbes respire as they break down dead plants So using up the (dissolved) oxygen Animals/fish living in the water die as a result Environment – Answer the Following • Describe what is meant by bioaccumulation and how it arises B1 Environment – Answer the Following • Describe what is meant by bioaccumulation and how it arises 1. Bioaccumulation – the increase in concentration chemicals in animal tissues 2. As you move up the food chain 3. Caused by chemicals which are not broken down by cells 4. Becomes toxic higher up the food chain 5. Results in death/reduced fertility Environment – Answer the Following • Draw a typical pyramid of biomass for a food chain consisting of 3 organisms and explain why it will always have this shape. B1 Environment – Answer the Following • Draw a typical pyramid of biomass for a food chain consisting of 3 organisms and explain why it will always have this shape. 1. Drawing Always pyramid shape because: 2. Much of the biomass/energy consumed by an organism is NOT used for growth 3. So NOT passed on to the next stage in the food chain 4. Energy used in movement/maintaining body temp Environment – Answer the Following • Outline the main processes that contribute to the carbon cycle (you may wish to draw the cycle first). B1 Environment – Answer the Following • Outline the main processes that contribute to the carbon cycle (you may wish to draw the cycle first). 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Photosynthesis – Where carbon dioxide is removed from air by plants Respiration – Which carbon dioxide in released into the air Feeding – Which transfers carbon from plants to animals Death – Which provides materials for organisms to decay Decay – The break down of waste materials by respiring microbes Environment – Answer the Following • Outline the main processes that contribute to the nitrogen cycle (you may wish to draw the cycle first). B1 Environment – Answer the Following • Outline the main processes that contribute to the nitrogen cycle (you may wish to draw the cycle first). 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Some bacteria convert nitrogen in the air to nitrates in soil Nitrates in the soil are used by plants to make protein Animals obtain nitrogen by eating plant proteins Animal waste returns nitrogen to the soil as urea/in faeces Nitrogen returned to the soil when animals die as a result of decay by microorganisms Which first convert to ammonia Before soil bacteria convert the ammonia into nitrates Other soil bacteria convert soil nitrates into nitrogen in the air Inheritance – Answer the Following • What is meant by ‘genetic/DNA profiling’ and describe how it works. B1 Inheritance – Answer the Following • What is meant by ‘genetic/DNA profiling’ and describe how it works. 1. 2. 3. 4. Used to show similarity between two DNA samples DNA cut into short pieces Then separated into bands Pattern of bands is unique to each individual (except genetically identical twins) 5. So can be used for identification 6. Related individuals have similar pattern/share bands 7. so can be used for classification/paternity cases Inheritance – Answer the Following • Draw a diagram and explain it to show how the probability of parents having a boy or a girl is 50:50. B1 Inheritance – Answer the Following • Draw a diagram and explain it to show how the probability of parents having a boy or a girl is 50:50. Inheritance – Answer the Following • Describe the process involved in producing a herbicide resistant GM crop and why it is useful for the farmer B1 Inheritance – Answer the Following • Describe the process involved in producing a herbicide resistant GM crop and why it is useful for the farmer 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Herbicide resistant gene cut out from one plant Gene transferred to a crop plant Crop can be sprayed with herbicide and be unaffected So only weeds are killed Reducing competition (for space/nutrients) Thus increasing yields Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • What is meant by variation, what causes is, and describe the differences between continuous and discontinuous variation. B1 Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • What is meant by variation, what causes is, and describe the differences between continuous and discontinuous variation. 1. Variation – differences between individuals 2. Caused by environment or genetic causes (both needed) 3. Continuous – where an individual can be at any point along a range of variation 4. Shown as a bell shaped curve of a (line) graph 5. Discontinuous – where an individual can only be at distinct categories of variation 6. Shown as a bar graph Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • Describe the differences between sexual and asexual variation. B1 Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • Describe the differences between sexual and asexual variation. 1. Asexual has one parent whereas sexual has two 2. Asexual produces clones/genetically identical offspring whereas sexual produces genetically similar/different offspring 3. Asexual uses mitosis only whereas sexual requires meiosis 4. Asexual does not require gametes/sperm and egg/sex cells whereas sexual does Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • What is meant by ‘gene therapy’? Describe how it is carried out in the case of cystic fibrosis and what its limitations are. B1 Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • What is meant by ‘gene therapy’? Describe how it is carried out in the case of cystic fibrosis and what its limitations are. 1. Involves inserting the normal version of a gene into affected tissue 2. Faulty cystic fibrosis gene results in sticky mucus blocking bronchioles 3. Caused by recessive allele 4. Normal gene is inserted into lung tissue using inhaler Problems 5. Gene isn’t always expressed/switched on 6. Hard to target the right cells 7. Not a cure for the condition Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • What is evolution and describe the stages of natural selection which bring evolution about. B1 Variation and Evolution – Answer the Following • What is evolution and describe the stages of natural selection which bring evolution about. 1. Evolution – idea that species change over time Natural selection 2. Individuals within species show a wide range of variation 3. Due to differences in their genes 4. Those with advantageous characteristics more likely to survive 5. And therefore reproduce 6. And therefore pass on the genes for those characteristics to their offspring 7. Over time those genes become more common (whilst disadvantageous genes become less common) Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • In what ways do plants respond to their environment? B1 Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • In what ways do plants respond to their environment? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Respond in the way that they grow Controlled by plant hormones Gravitropism – response to gravity Roots grow towards pull of gravity Shoots grow away from pull of gravity Phototropism – response to light Shoot grow towards light On order to photosynthesise Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • How does a person ensure that their blood sugar level stays relatively constant? B1 Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • How does a person ensure that their blood sugar level stays relatively constant? When blood sugar/glucose level too high 1. Pancreas 2. Releases insulin (into blood) 3. Liver responds 4. By absorbing glucose and converting to (insoluble) glycogen 5. For storage Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • What is diabetes and how can it be treated? B1 Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • What is diabetes and how can it be treated? 1. A condition in which blood glucose may rise to fatally high level 2. Because body does not produce enough insulin (type 1) 3. Diagnosed by detecting glucose in urine 4. Treated by injecting insulin 5. And following low sugar/carbohydrate diet 6. Could also be treated by pancreatic transplant Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • Describe and explain how the body responds when it gets to hot. B1 Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • Describe and explain how the body responds when it gets to hot. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Blood flows to the skin surface So heat leaves body Hairs lie flat So no insulating air layer Sweat is produced As sweat evaporates it uses heat from the body Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • Describe and explain how the body responds when it gets to cold. B1 Response and Regulation – Answer the Following • Describe and explain how the body responds when it gets to cold. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Blood stays away from the skin surface So less heat leaves body Hairs stand erect So creating an insulating air layer Shivering occurs Which is an involuntary muscle contraction That generates heat Health – Answer the Following • Explain why sugar and fat are components of food that are a cause for concern. B1 Health – Answer the Following • Explain why sugar and fat are components of food that are a cause for concern. Sugar and Fast 1. Both high-energy foods so can lead to obesity 2. Obesity can lead to heart disease Sugar 3. Remains on teeth and provides food for bacteria 4. Resulting in tooth decay Fat 5. Animal fats form cholesterol in body 6. Which is deposited on the inside of blood vessels 7. And can lead to heart disease Health – Answer the Following • What are the causes of obesity and why is it a problem? B1 Health – Answer the Following • What are the causes of obesity and why is it a problem? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Caused by an unhealthy diet And lack of exercise Increases risk of heart disease And cancer And joint problem And type 2 diabetes Type 2 diabetes controlled by tablets rather than insulin injections Health – Answer the Following • Using alcohol as an example describe what is meant by the word ‘drug’ and why they might be problematic. B1 Health – Answer the Following • Using alcohol as an example describe what is meant by the word ‘drug’ and why they might be problematic. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A drug is a substance which alters the way the body works Alcohol increases reaction time/slows reactions People may become addicted to/dependent on alcohol Meaning the suffer withdrawal symptoms without it Alcohol can cause long term damage (should include at least one example from liver, circulatory or heart disease) Health – Answer the Following • What problems may arise in developing new medicinal drugs and how might these be avoided? B1 Health – Answer the Following • What problems may arise in developing new medicinal drugs and how might these be avoided? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Drugs may have side affects Side effects may not show up until lots of people use them So lots of testing must be done Some testing may involve testing on animals Some object as they think it unethical