* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
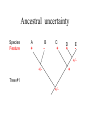
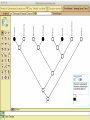
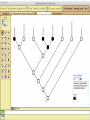
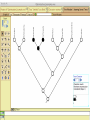
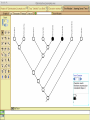
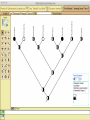
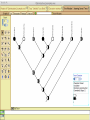
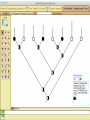
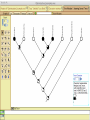
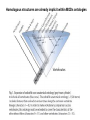
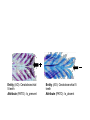
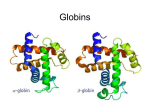
Homology Homology Review Which of the following structures are homologous? Definition: Structures (including genes) are homologous if they evolved from some structure in a common ancestor Homologous forelimbs not homologous as forelimbs or wings Human arm Lobed-fin fish fin Bat wing Bird wing not homologous as wings Insect wing Wings are functionally classified, and are analagous structures Why do we care about homology when building an anatomy ontology? Consider an anatomy ontology of vertebrates: skeletal system cranial skeletal system parietal bone (in_organism human) parietal bone (in_organism zebrafish) frontal bone (in_organism human) frontal bone (in_organism zebrafish) f pa Homologous : frontal bone (zebrafish) and parietal bone (human) Different genes and developmental processes may underlie the development of the zebrafish frontal and the human frontal, even though they have the same name and are similarly located Homologous_to A1 in B1 homologous_to A2 in B2 iff exists A3, B3: A1 in B1 descends_from A3 in B3 & A2 in B2 descends_from A3 in B3 (Note B1 and B2 must both be subclades of the clade descending* from D) (*In the genealogical sense) Note: Do we need to include time (exists & existed)? FN – just to be on the safe side we can include time – it's not usefu [edit] relation to what is in RO proposed Directly_descends_from x1 directly_descends_from x2 iff there are y1, y2 such that: - y1 is an organism - x1 is an anatomical structure - x1 part_of y1 - y2 is an organism - x2 is an anatomical structure - x2 part_of y2 - y2 is a parent of y1 -the genetic sequence that determined the morphology of x1 is partially a copy of the genetic sequence that determined the morphology of x2. descends_from is the instance level relation which is the transitive closure over directly_descends_from Descends_from A in B descends_from C in D : For all A(a) -> exists b, d, c: B(b) & C(c) & D(d) a part_of b a descends_from c c part_of d (Note – B must be a subclade of the clade descending* from D) Note that there are a number of synonyms for descended_from, including 'evolutionarily_derived_from' which is currently in ROproposed as follows: id: OBO_REL:evolutionarily_derived_from name: evolutionarily_derived_from def: "Instance 3-ary relation: x edf y as T iff x specified_by gx and gx ancestral_copy_of gy and gy specifies y" [] synonym: "derived_from" RELATED [] synonym: "descended_from" RELATED [] synonym: "evolved_from" RELATED [] is_transitive: true What are Characters? a,b - symphysial bone margins straight c - anterior symphysial bone margin concave, resulting in oval gap between bone halves Character “optimization” • Method to infer ancestral conditions (features) – Inferred ancestral condition dependent on phylogenetic tree – I.e. different trees may imply differently reconstructed ancestors Ancestral uncertainty Species Feature A + B - C + D + E +/- +/- + Tree #1 +/- Ancestral certainty Species Feature A + C + B - D + E +/- Tree #2 +/- + Heart presence/absence optimized on Bilaterian tree + + +/+ _ +/No heart +/+_ in ancestor No +/+_ of Bilateria _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ + _ _ _ +/_ _ _ + __ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ I. Bilaterians Phylogeny from Garey, 1999 Character Optimization • Tree - including an ‘out group’ • Character Matrix - states for taxa at tips of tree • Assign values from column of matrix to tree • ‘Polarize’ the state at the root using the outgroup Homology Evidence Codes • • • • • • Inferred from morphological similarity Inferred from positional similarity Inferred from developmental similarity Inferred from compositional similarity Inferred from gene expression similarity Inferred from phylogeny Use case: Query for phenotypes affecting the human frontal bone and its homologous structure in other species. Homologs = Synonyms How and where should homology information be captured? Homology between genes is already determined and recorded by the model organism community Gene homology Types of gene homology: •Genes that diverged due to a speciation event are termed orthologs • Genes that diverged due to a duplication within a species are termed paralogs Gene orthology is recorded using different types of evidence: FuguA Conserved location: HOXB mouse Kim et al., 1999 Homology between anatomical structures is already determined and but not yet captured in a database the evolutionary community Homology assignments are based on specific kinds of evidence IP: Inferred from Position ID: Inferred from Development IC: Inferred from Composition Each homology assignment is associated with reference to a physical piece of evidence, a person, or literature. Homology statements include evidence and citations, and different homology statements are used to create and refine phylogenies. Homologous structures are already implicit within MODs ontologies Discussion points 1. Do we need a relationship in OBO-REL to define homology? This is a symmetric relation between sisters and it is the relationship that requires evidence and attribution. 2. Should homology assignments be a top-down or bottom up approach?eg. Pairs of taxa vs. CARO-centric assignments? RE:domain experts are required. It might be easier to enlist help in a pairwise manner. 3. Homology needs to be captured for similarity searches. Text or synonym searches are insufficient. Does CARO take into account homology or is it a separate data set? 4. If two structures are deemed homologous, how does this information transfer down is_a chains? Need use cases. Entity (AO): Ceratobranchial 5 teeth Attribute (PATO): Is_present Entity (AO): Ceratobranchial 5 teeth Attribute (PATO): Is_absent