* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
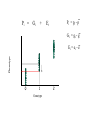
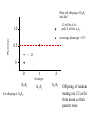
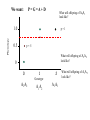
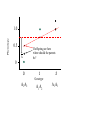
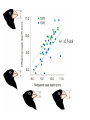
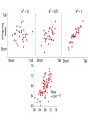
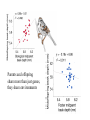
_ Pi = Gi + Pi = pi - p Ei _ Gi = gi - g _ Phenotype Ei = ei - e 0 1 Genotype 2 Pi = Gi + Ei What is: Some algebra: Pi 2 = (Gi + 1 1 2 Pi ( pi p ) 2 n i n Ei)2 = variance of phenotype Sum over all individuals: P i 2 (G i + Ei )2 i Take the mean: 1 1 2 Pi (G i + n i n Ei ) 2 1 1 2 Pi (G i + n i n 1 1 1 2 2 Pi G i + n i n n Ei ) 2 1 2 Pi = variance P n i 1 Ei 2 Gi Ei n 2 Variance P = Variance G + Variance E + something else Pi = Gi VP = + Ei true for individuals VG + VE + 2 Cov (G,E) true for populations Pi = Gi + Ei VP = VG + VE When the Phenotype is the sum of the Genotype and the Environment, then the Variance in Phenotypes is the sum of the Variances in Genotype and Environment. (plus the covariance term, which we will come back to later) Look at G only for a while What is this phenotype? 1.0 Let freq A1 = 0.5 Phenotype pi = .5 _ What is p ? =0.5 0.5 What is phenotype? pi = 0 0 What is this phenotype? pi = -.5 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 pi = -0.5 A1A2 A1A1 0 0.5 What will offspring of A1A1 look like? 1/2 will be A1A2 and 1/2 will be A1A1 Phenotype 1.0 on average phenotype = 0.75 0.5 = .25 0 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 For offspring of A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 Offspring of random mating are 1/2 as far from mean as their parents were Additive Phenotype 1.0 Genotype score gives us the phenotype Offspring are 1/2 as ‘deviant’ as parents Well-behaved inheritance 0.5 0 P=G =A 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 Dominance What is the mean phenotype? = 0.75 Phenotype 1.0 0.5 Now the genotype score does not give us the phenotype. 0 P A 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 Offspring still resemble their parents and it would still be very useful to be able to determine what is inherited. We want: P=G =A+D What will offspring of A1A1 look like? Phenotype 1.0 p=1 0.5 p = .5 What will offspring of A2A2 look like? 0 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 What will offspring of A1A2 look like? We want: P=G =A+D A Phenotype 1.0 If offspring are here where should the parents be? 0.5 Additive: Offspring are 1/2 as ‘deviant’ as parents Well-behaved inheritance 0 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 Phenotype 1.0 0.5 If offspring are here where should the parents be? A 0 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 Phenotype 1.0 0.5 Now we have a component, the Additive component that predicts what the offspring will be 0 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 However we still want: P = G = A + D What is D? Phenotype 1.0 0.5 A = 0, D = .25 0 A = .5, D = -.25 A = -.5, D = -.25 0 1 2 Genotype A2A2 A1A2 A1A1 Now we have P = A + D Pi = Gi VP = + Ei VG + VE Pi = Ai + Di + VP Ei = VA + VD + VE + some other stuff (covariances) Additive and Dominance components are both genetic However, dominance is not inherited--it is a relationship between alleles only one of which is inherited. Additive component is inherited. When an individual reproduces only half of its genes (sexual reproduction) are transmitted. The additive component is relevant for natural selection. (It is what is inherited.) Mean of y Covariance Each point is (xi, yi) Mean of x 1 ( xi x )( yi y ) Cov( x, y) n i 1 1 2 Pi (G i + n i n 1 1 1 2 2 Pi G i + n i n n VP = Ei ) 2 1 Ei 2 Gi Ei n 2 VG + VE + 2 Cov (G,E) What is Cov (G,E)? Say: “Gene-Environment Covariance” “G by E” What happens to the Phenotypic Variance if there is a substantial G by E term? Suppose genetic variation for size in plants and two types of environment--one that makes them large and one that makes them small. If plants with genes for small size are found in places that make plants small (and vice versa) what is the sign of the G by E term? What about the converse? What sort of experimental techniques eliminate G by E? Offspring What about parents and offspring? Parents When offspring resemble parents their phenotypes covary Offspring Let us ignore E for a moment Parents 1 cov( P, O) ( pi p )(oi o ) n What is (pi -p) ? = Ai + Di What is (oi - o) ? = 1/2 Ai The product = 1/2 Ai2 + 1/2 Ai Di The mean over all pairs = 1/2 VA + 1/2 Cov (A,D) = 1/2 VA Offspring Cov(Offspring,Parents) = 1/2 VA Parents Heritability, h2 is defined as: The proportion of phenotypic variance that is additive VA h2 VP Offspring Suppose we want to predict the phenotype of the offspring from the phenotype of the parents. Parents Regression want to predict y from x We produce a regression coefficient or slope for a line The line goes through the mean x and mean y Regression coefficient = cov XY VA (1 / 2) (1 / 2)h 2 Var x VP Offspring Offspring have two parents Which to choose? Use the average, call it the Midparent Parents Variance of midparents is less than variance of one parent (the variance of an average is always less) VMidparent = 1/2 VP, therefore regression of offspring on Midparent = cov OM VA h2 VarM VP h2 = 0.7-0.8 h2 ~ 0.5 offspring mean h2 ~ 0 = h2 h2 ~ 1 Parents and offspring share more than just genes, they share environments Pi = Ai + Di + = VA + VD + VE + some other stuff (covariances) What is parental phenotype? Pi = Ai + Di + EiP Offspring VP Ei What is offspring phenotype? Oi = 1/2 Ai + EiO Parents CovO,P = 1/2 VA + 1/2 Cov (A,D) + 1/2 Cov (A,EP ) + Cov (A,EO ) + Cov (D,EO ) + Cov (EP,EO ) CovO,P = 1/2 VA + “G by E terms” + covariance in environment Sibling Siblings have the same parents Sibling They have resemblance through to parents---AND it is possible for both to get the same alleles. In that case their phenotypes will be influenced by Dominance in the same way. Covsiblings = 1/2 VA + 1/4 VD Offspring How does a population respond to selection? On average, Offspring = h2 Parents Mid-Parent If we only allow some parents to breed (e.g. above the mean) Then the offspring will be larger. By how much? offspring = h2 Parents R = h2 s Mean of Parents Threshold for Survival s Mean of Surviving Parents Mean of Offspring R R = h2 s Often: h2 = R / s s -- Selection Differential With a single gene the change in phenotype is the change in allele frequency: sq 2 (1 q) q 1 sq 2 With a quantitative trait: R = h2 s How big are selection differentials? R = h2 s Selection differentials How much heritability is there? Why is that important? How do traits differ? R = h2 s Or resemblance among relatives