* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cloning of the TCR b-chain gene by subtractive hybridization
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
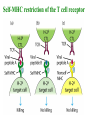
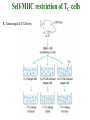
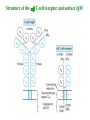
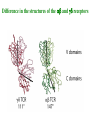
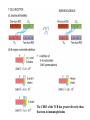
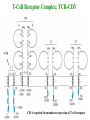
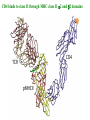
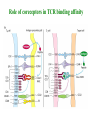
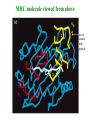
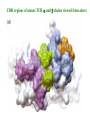
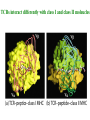
Self-MHC restriction of the T cell receptor Self-MHC restriction of TC cells R. Zinkernagel & P. Doherty Cloning of the TCR b-chain gene by subtractive hybridization By S. M. Hedrick & M. M. Davis 3 important assumptions made by Hedrick and Davis: • The TCR mRNA would be associated with membranebound polyribosomes like the mRNAs that encode other integral membrane proteins. (eliminate ~97% mRNAs) • 98% of the genes expressed in lymphocytes are common to B and T cells. TCR should be in the 2% genes expressed specifically in T cells. (DNA subtractive hybridyzation eliminates 98%) • TCR genes should undergo DNA rearrangements like those observed in the Ig genes of B cells. Structure of the ab T-cell receptor and surface IgM Difference in the structures of the ab and gd receptors Limited diversity Organization of mouse TCR gene segments A productive rearrangement of the a chain gene segments deletes Cd TCR variable- region genes rearrange in a manner similar to Ig gene Junctional diversity The CDR3 of the TCR has greater diversity than that seen in immunoglobulins T-Cell Receptor Complex: TCR-CD3 or ζη CD3 is required for membrane expression of T cell receptors Structures of the CD4 and CD8 coreceptors or aa dimer CD8 binds to class I by contacting MHC class I a2 and a3 domains CD4 binds to class II through MHC class II a2 and b2 domains Affinity of TCR for peptide-MHC complexes is weak compared with antibody binding T cell-APC interactions are strengthened by cell-adhesion molecules, including CD2, LFA-1, CD28, and CD45R Role of coreceptors in TCR binding affinity The ternary complex Of mouse TCR Bound to MHC Class I and peptide CDR3 CDR3 MHC molecule viewed from above not in contact with peptide CDR regions of mouse TCR a and b chains viewed from above TCRs interact differently with class I and class II moleucles Alloreactivity of T cells: in addition to self-MHC plus antigens, T cells also respond to foreign MHC molecules, a reaction that leads to rejection of allogeneic grafts (transplants in the same species) Alloantigens: epitopes present on molecules that differ among members of the same species because of genetic variation. T cells recognize a foreign MHC molecules directly. ~1-5% of all T cells are reactive to alloantigen.