* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Punnett Square Notes
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
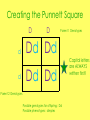
Punnett Square Notes Crossing Traits • We use Punnett Squares to cross parents traits. This gives us a percentage to be able to determine an offspring’s possible traits. • We represent traits with letters. • Dominant traits are represented with a capital letter. • Recessive traits are represented with a lower case letter. • Since each parent passes on half of an offsprings traits, each person has two letters, one from mom and one from dad. We refer to these letters as “alleles”. Expressing Traits • If an offspring possesses the dominant trait, it can be expressed one of two ways: DD or Dd • Recessive traits can only be expressed as: dd Naming • Each one of these ways has a specific name. – DD homozygous dominant both alleles are the same a dominant gene was passed on – Dd heterozygous OR heterozygous dominant alleles are different a dominant gene was passed on – dd homozygous recessive both alleles are the same only recessive genes were passed on Other Vocab • purebreed: homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive • hybrid: heterozygous • genotype: trait represented by letters – Genetic makeup • phenotype: the physical representation of the genotype – How we see the traits Putting it all together Example 1: Trait: Dimples (having dimples is dominant, NOT having dimples is recessive) Mom: homozygous dominant -genotype: DD -phenotype: dimples Dad: homozygous recessive -genotype: dd -phenotype: NO dimples Creating the Punnett Square D d d D Parent 1 Genotypes Dd Dd Dd Dd Parent 2 Genotypes Possible genotypes for offspring: Dd Possible phenotypes: dimples Capital letters are ALWAYS written first!! Putting it all together Example 2: Trait: Freckles (having freckles is dominant, NOT having freckles is recessive) Mom: homozygous recessive -genotype: ff -phenotype: NO freckles Dad: heterozygous -genotype: Ff -phenotype: freckles Creating the Punnett Square F f f f Possible genotypes for offspring: Ff ff Ff Ff Possible phenotypes: freckles no freckles ff ff What are the chances of a child having freckles? 2 out of 4 OR 50% What are the chances of a child NOT having freckles? 2 out of 4 OR 50%