* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download aminoacids
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
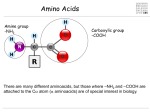
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Food Why food? – – Our body performs many processes and has necessary infra-structure for this performance Energy is needed to – 1 Perform these processes Build necessary infra-structure Sustain the molecular organization Food provides this much needed energy Aminoacids What is food Food consists of six basic ingredients – – – – – – 2 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Vitamines Minerals Water Aminoacids Carbohydrates Include sugars and sugar polymers (starch and glycogen) etc. – – 3 Generally used for generation of energy Some role in structure Polymeric forms undergo digestion Aminoacids Lipids Include oils and fats etc – – 4 Second most preferred source of energy after carbohydrates Some structural role e.g. biomembranes Undergo digestion Aminoacids Proteins 5 Undergo digestion to split into aminoacids The least preferred role in energy generation Perform a large number of roles, however, major role in structure and catalysis Aminoacids Vitamins 6 Cofactors for many enzymes No role as energy substrate No digestion (directly absorbed) Aminoacids Minerals 7 Major role chemical reactions particularly oxidation/reduction reactions No digestion, directly absorbed Aminoacids Water 8 Serve as solvent No digestion, directly absorbed Aminoacids Proteins 9 Proteins are made up of 20 different types of aminoacids Dietary proteins are digested to yield aminoacids These aminoacids are absorbed by the intestine and transferred to blood stream Aminoacids enter into different body cells from blood circulation In cells, aminoacids are then bonded together to from specific proteins (tissue /species specific) These proteins then perform various but important functions of the cell/body Aminoacids Aminoacids 10 Aminoacids Types of Aminoacids Protein & Non-protein aminoacids (Standard & Non-standard aminoacids) Protein Aminoacids are further classified on the basis of – The nature of their side chains 11 Polar or non-polar Aromatic or non-aromatic Function groups (hydroxyl, thio, methyl-thio) Capability of Synthesis (Essential or Non-essential) Aminoacids Definition 12 Organic compounds containing an amino and a carboxylic acid Aminoacids Building Blocks of Proteins Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins There are 20 different aminoacids used for proteins synthesis in all living organisms An α-amino acid consists of a – – – – – 13 central carbon atom, called the α carbon, linked to an amino group, the α amino group a carboxylic acid group, the α carboxylic group a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive R group called the side chain. Aminoacids Amino acid Isomers • With four different groups α -amino acids are chiral (except glycine) − 14 forms two mirror-image forms the L isomer and the D isomer Aminoacids Ionization of Amino Acids 15 Only L amino acids are used in proteins Aminoacids are ionized in solution Aminoacids Ionization of Amino Acids At acidic pH – – At neutral pH – – Amino group is protonated (NH3+) _ Carboxyl group is deprotonated (COO ) At basic pH – – 16 Amino group is protonated (NH3+) Carboxyl group is not deprotonated (COOH) Amino group is not protonated (NH2) _ Carboxyl group is deprotonated (COO ) Aminoacids General Formula of an Amino Acid R= -H, -CH2, -CH2OH, C2H4OH etc 17 Aminoacids Side Chain Variations 18 Size Shape Charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity Aminoacids Classification of Amino Acids 19 Aminoacids Uncharged (Non-Polar) Amino Acids Uncharged (10) Achiral (1) G Simple Chain(4) AVLI 20 Chiral (9) Sulfur Cont. (2) CM Aromatic (2) Phe T Heterocyclic (1) P Aminoacids Glycine 21 Simplest amino acid Side chain only a H atom A chiral (optically inactive) Aminoacids Physiological Roles-Glycine Part of tripeptide coenzyme “Glutathione”, which protects –SH group from oxidation Takes part in synthesis of heme, purines and creatin Detoxication of benzoic acid to make a soluble conjugate, the hippuric acid Formation of bile salts by conjugation to cholic acid (glyocholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid) Can be converted to other aminoacids e.g. serine, which may be converted to pyruvate (glucogenic aminoacid) Glycine oxidase conver glycine into glyoxalic acid, which is oxidized to form formic acid and oxalic acid – – Formic acid becomes a part of 1-carbon metabolism Oxalic acid is excreted in urine 22 Excess formation leads to “Hyperoxalurea” resulting in formation of Caoxalate which precipitates in urinary tract Precipitation results in Urinary Calculi and Calcification of kidneys. Aminoacids Non-Polar Amino Acids 23 Progressively larger side chains Isoleucine contains an additional chiral center Stabilize protein structure in aqueous solutions Aminoacids Physiological Roles-Valine Undergoes – – This results in the formation of – – 24 transamination followed by decarboxylation isobytyryl-CoA ultimately converted into Succenyl-Co-A, an intermediate of TCA cycle Aminoacids Physiological Roles-Leucine Undergoes oxidative transamination to ultimately form – HMG-CoA may be converted into – – 25 HMG-CoA Cholysterol Acetoacetate/Acetyl-CoA (so a ketogenic aminoacid) Aminoacids Physiological Roles-Isoleucine Undergoes oxidative transamination to form – HMG-CoA may be converted into – – 26 HMG-CoA Cholysterol Acetoacetate/Acetyl-CoA (so a ketogenic aminoacid) Aminoacids Proline 27 Imino acid Heterocyclic: contains a pyrrole ring (pyrrolidine derivative) Side chain bonded to α amino group Causes bends in protein structure May form 4 hydroxyproline as a result of post-transcriptional modification perhaps only in collagen A small proportion may also occur as 3-hydroxyproline too Interchangeable with ornithine, thus it can contribute to urea cycle Can give rise to glutamate Aminoacids Sulfur Containing Amino Acids 28 Met is always first amino acid of a nascent protein Cys may be involved in forming disulfide bridges Aminoacids Sulfur Containing Amino Acids 29 A disulfide bridges between to cysteines to form a Cytine Aminoacids Aromatic Non-polar Amino Acids 30 Phe is purely hydrophobic but Try is less so Strongly absorb UV light (Amax 280λ) Aminoacids Phenylketonurea 31 It is an autosomal recessive disorder A disorder caused due to deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase Frequency 1 in 20,000 Blockage of conversion to tyrosine results in ~20 fold increase in Phe. Concentration of phenylpyruvate increases resulting in excretion in urine Addition of ferric chloride to urine turns it olive green Phenylketonuric are severally mentally retarded, if not properly treated Low Phe diet is solution to the problem Aminoacids Classification of Polar Amino Acids 32 Aminoacids Charged Amino Acids Charged (10) Polar (5) Hydroxyl group (3) Basic (3) Arg His Lys Acidic (2) Asp Glu Amide group (2) Asn Gln Aliphatic (2) Ser Thr Aromatic (1) Tyr 33 Aminoacids Polar aminoacids Aminoacids containing hydroxyl group May be post-transcriptionally phosphorylated Ser/Thr and Tyr phophorylation are very important in Cellular signaling cell cycle regulation and tumor development 34 Aminoacids Serine 35 Precursor for the synthesis of cysteine, choline and cephalins Takes part in the synthesis of nucleic acid bases Can be converted into glycine and pyruvic acid Serves as carrier of phosphorus in phosphoproteins Aminoacids Threonine 36 Can be converted into glycine Can be converted in propionyl-CoA and then to succinyl-CoA Serves as carrier of phosphorus in phosphoproteins Aminoacids Tyrosine 37 Obtained from phenylalanine Can be converted to dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and Dopamine Dopamine is precursor of catecholamines (adrenaline and nor-adrenaline) Tyrosine is also a precursor for T3 and T4 Skin pigment, melanin is also a produce to tyrosine metabolism Aminoacids Basic Aminoacids 38 Aminoacid group of these aminoacids gets ionized in acidic pH range They may make part of active site Basic aminoacids include lysine, argenine and histidine Aminoacids Lysine 39 It is a basic aminoacid It is among essential aminoacids It does not allow α-helix to be formed/continued Aminoacids Argenine 40 Its hydrolysis yields urea Takes part in urea cycle Contributes in the formation of creatine An essential aminoacid Does not allow formation of α-helix Aminoacids Histidine 41 Contains an imidazole ring Near neutral pH the imidazole ring gets charged It is often found in the active site of enzymes Imidazole ring can act as electron acceptor/donor in an enzyme catalyzed reactions Aminoacids Acidic aminoacids 42 These aminoacids contain an additional –COOH group They get ionized in the basic pH range Their side chains may act as proton acceptor They may make part of active site of an enzyme They may accept an amino group to become amides i.e. asparagine and glutamine Glutamine play important role in nitrogen transport/urea cycle Aminoacids Essential Aminoacids 43 Aminoacids Aminoacids in special sources 44 Non-protein aminoacids May be a part of some molecules Play important role in physiological functions Aminoacids 1,2. Citruline and ornithine Found in liver Intermediates of urea cycle Take part in conversion of NH3 to urea NH2 H-N-(CH2)3-CH-COOH C=O NH2 H2N-(CH2)3-CH-COOH Ornithine NH2 Citrulline 45 Aminoacids 3. β-alanine Part of vitamin B (pantothenic acid) H2N-CH2-CH2-COOH 46 Aminoacids 4. Pantothenic acid A widely distributed vitamin Make a part of co-enzyme A (Co-A) Take part in a large number of metabolic reactions CH3 O CH2—C—CH—C—NH—CH2—CH2—COOH OH 47 CH3 OH Aminoacids 5. γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) GABA is a neurotransmitter Found in nervous tissue H2N-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH 48 Aminoacids 6. 49 Dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) A metabolite of phenylalanine and tyrosine L-DOPA is used in treatment of Parkinsons Disease OH OH Aminoacids 7. Homocystine Formed by de-methylation of methionine H 50 Aminoacids 8. 51 Iodinated aminoacids Mono-iodotyrosine (MIT) and Di-iodotyrosine (DIT) are intermediates in thyroxin synthesis Tri-iodothyronine (T-3) and Tetra-iodothyronine (T4) are thyroxins (thyroid hormones) I I I I Aminoacids The End 52 Aminoacids