* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3. DarkReaction
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
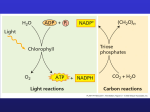
The Dark Reaction - light-independent - energy stored in ATP and NADPH (from light reaction) is used to reduce CO2 to sugar Three independent ways to reduce CO2 to make sugar: 1. the Calvin cycle (C3), 2. C4 photosynthesis, 3. crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM). The Calvin Cycle 1. CO2 is fixed by rubisco 1. 2. CO2 + RuBP unstable C6 2 PGA Reduction of CO2 to make G3P - 3. Uses ATP and NADPH G3P is exported to cytoplasm to make starch, sucrose, oils Regenerating RuBP 1. - for enery 12 molecules of G3P made in the Calvin cycle two are “released” 2. - the Calvin cycle needs to “turn” 6 times to make one glucose!!! G3P - one-third forms starch - two-thirds are converted to sucrose and then hydrolyzed in other parts of plant into glucose and fructose - Ultimately used as a source of C for nucleic acids, amino acids, fats… Rubisco ● ● ● ● Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase fixes CO2 & O2 Enzyme in Calvin Cycle (1st step) Most abundant protein on Earth – About 50% total plant protein! Stomata - lungs openings on the surface of the leaf that allow the exchange of gases between air spaces in the leaf and the atmosphere Guard cells – control the size of the stoma in response to environmental conditions ● ● ● ● The size of the guard cell changes when water moves into or out of the cell K+ ions are actively pumped into the guard cell and water follows by osmosis Light, and CO2 concentration affect the movement of K+ ions into the cells Generally stomata are open during the day and closed at night Photorespiration ● the reaction of RuBP with oxygen, reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis ● ● ● rubisco is inefficient: “fixes” O2, as well as CO2 C3 plants lose 20% of their energy to fix one CO2 this gets worse with heat! - Under hot and dry conditions (daytime) plants will close their stomata to prevent water loss - This causes a build up of oxygen since CO2 can’t enter…so MORE photorespiration Avoiding Photorespiration ● ● ● C3 – The majority of plants C4 – CO2 temporarily stored as 4-C organic acids resulting in more more efficient C exchange rate – Advantage in high light, high temperature, low CO2 – Many grasses and crops (e.g., corn, sorghum, millet, sugar cane) CAM – Stomata open during night – Advantage in arid climates – Many succulents (e.g. cacti) Fig. 10.21 Comparison of Photosynthesis in C3 and C4 Plants VARIABLE C3 PLANTS C4 PLANTS Photorespirati on Extensive Minimal Perform Calvin cycle? Yes Yes Primary CO2 acceptor RuBP PEP CO2-fixing enzyme Rubisco (RuBP carboxylase/oxyge nase) PEP carboxylase and rubisco First product of CO2 fixation 3PG (3-carbon compound) Oxaloacetate (4carbon compound) Affinity of carboxylase for CO2 Moderate High Photosynthetic Mesophyll cells of leaf Classes of chloroplasts One Mesophyll + bundle sheath Two - - - C3 photosynthesis: about 3.5 billion years ago, C4 plants appeared about 12 million years ago. A possible factor in the emergence of the C4 pathway is the decline in atmospheric CO2 CAM PLANTS - CAM is similar to C4 - CO2 is fixed to a 4-carbon compound - Separated by time rather than space: At night cooler and water loss is minimized stomata open and CO2 is fixed in mesophyll cells to form the 4- carbon oxaloacetate, which is converted into malic acid. During the day when the stomata close to reduce water loss, the accumulated malic acid is shipped to the chloroplasts to form sugars Fig. 10.22 CAM Plants Global Environmental Change & Photosynthesis: C3 vs. C4 vs. CAM ● ● ● Increasing CO2 Increasing chronic and acute temperatures Changes in water *At high CO2, C3 more efficient than C4 at all temps. (photosynthesis only, not other processes)