* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Molecules of Life
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
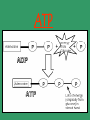
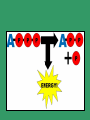
The Molecules of Life There are four main compounds that create and support life called macromolecules: Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Lipids These are fats. They are an important component of cell membranes and make up many steroids and other signaling compounds in the body. Protein These are long chains of amino acids add together to make the structures of the body. They are also enzymes that allow chemical reactions happen. Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA. They store genetic information. More on them later. Carbohydrates Sugars They are the fuel the body uses to sustain itself. The most important one to know is Glucose – a simple sugar that the body ‘burns’ to create its energy or ATP. ATP This molecule is what we referred to when we said the mitochondria makes energy. The mitochondria actually make ATP, a molecule that can store (and later release) energy in the chemical bonds between its phosphates. ATP So, ATP = Energy! ATP ADP + Energy from the sugar Glucose = ATP Be the Scientist! Let’s say it’s the 1800s and you’re tasked with trying to understand how plants seem to grow to huge heights and immensely old ages without seeming to do anything more than drink water. Come up with some experiments that you could perform to uncover plants’ secrets. How do you think science discovered the secrets to how plants work? ATP