* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hcdc4 (archipelago) Endometrial Cancer
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
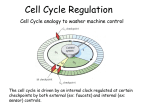
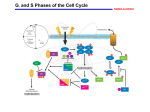
hcdc4 (archipelago) Endometrial Cancer Andrew Marshall April, 1, 2004 hcdc4 • • • Highly conserved throughout evolution – Ago (Drosophila), SEL-10 (nematode and mouse), and cdc4 (yeast) Locus – 4q.32 (mutated in 30% human tumors) F-Box and WD40 Domains (FBXW7) – Repeated sequences of W (tryptophan) and D (aspartic acid) (Strohmaier (2001)) hcdc4 and Cyclin E • Through various screens, we know the WD Domain serves as a dock for Cyclin E • Together with other molecules forms a functional SCF-type protein ubiquitination ligase What do we know about Cyclin E? Cyclin E and Cell Cycle Control • The up and down cycles of Cyclin E are responsible for the G1-S Transition • But how are these levels controlled? The Ubiquitination Cascade • Following the E1 to E2 and finally to E3 Ubiquitin Pathway – Thus, marking the target (cyclin E) with a polyubiquitin chain • Degradation by the Proteosome • Tumor Suppressor (negative regulator of cell proliferation) Putting It All Together What’s the Big Deal? • We Know – hcdc4 controls Cyclin E levels through the ubiquitin cascade – Cyclin E levels control the cell cycle – The cell cycle is..... Important Real Life Knockout Models Sorry… not that kind • The hcdc4 -/- (SEL-10) mouse is inviable – Halted development due to meiotic mistakes very early in development • Drosophila Model (Ago) – Over proliferation due to failure to exit cell cycle – Photoreceptor problems (Moberg 2001) Chromosomal Instability • Aneuploidy • Gene Amplification • Chromosome • • (Rajagopalan (2004)) Rearrangements, Inversions, Translocations, and Deletions Spindle Apparatus failure And in this Case, also Micronuclei Checkpoints • The Cell Cycle Must – Introduce no mistakes – Maintain diploidy • Am I Big Enough? • Am I OK? • A definitive association Prove It! between hcdc4 mutants and overexpression of Cyclin E – Without overexpression of Cyclin E mRNA • LOH • Restoration of correct cyclin E expression via retroviral transduction (Reed (2004)) (Strohmaier (2001)) Accumulation, Accumulation, Accumulation • Cancer takes more than one mutation • Increased chances with – Increased Cells • Increased proliferation due to constitutively active Cyclin E pushing cells from G1 to S (proliferative advantage) – DNA Problems • Chromosomal Instability due to that same push towards the S Phase • Accelerated lost of heterozygosity What Do We Get? Cancer! • More specifically, endometrial cancer – A cancer of the lining of the uterus Endometrial Cancer • How do we Really Know hcdc4/Cyclin E is the cause? (Spruck (2002)) Not So Fast • Not all endometrial cancers contain the hcdc4 mutation – 20% of cases with elevated Cyclin E levels – Although, Those that do are associated with increased metastasis and severity • Possible Reasons – Cyclin E regulated by different pathways – hcdc4 mutations of WD40 region and amino terminus • Different variants of hcdc4 (Cassia (2003)) Still a Mystery • Although a great deal of research has been done on hcdc4 of late, many of its functions remain to be understood • Notch Pathway • Alzheimer's – Different Targets and Different Roles Works Cited • Cassia, Raul, Moreno-Bueno, Gema, Rodriguez-Perales, Sandra, Hardisson, David, Cigudosa, Juan C., and Palacios M.D., Jose. Cyclin E gene (CCNE) amplification and hCDC4 mutations in endometrial carcinoma. The Journal of Pathology 201 589-595 (2003). • Moberg, Kenneth H., Bell, Daphne W., Wahrer, Doke C.R., Haber, Daniel A., and Hariharan, Iswar K. Archipelago regulates Cyclin E levels in Drosophila and is mutated in human cancer cell lines. Nature 413, 311-316 (2001). • Rajagopalan, Harith, Jallepalli, Prasad V., Rago, Carlo, Velculescu, Victor E., Kinzler, Kenneth W., Vogelstein, Bert, and Lengauer, Christoph. Inacivation of hCDC4 can cause chromosomal instability. Nature 428, 77-81 (2004). • Reed, Susanna Ekholm, Spruck, Charles H., Sangfelt, Olle, van Drogen, Frank, Mueller-Holzner, Elisabeth, Widschwendter, Marrtin, Zetterberg, Anders, and Reed, Steven I. Mutation of hCDC4 Leads to Cell Cycle Deregulation of Cyclin E in Cancer. Cancer Research 64, 795- 800 (2004). • Spruck, Charles H., Strohmaier, Heimo, Sangfelt, Olle, Muller, Hannes M., Hubalek, Michael, Muller-Holzner, Elisabeth, Marth, Christian, Widscwendter, Martin, and Reed, Steven I. hCDC4 Gene Mutations in Endometrial Cancer. Cancer Research 62, 4535-4539 (2002). • Strohmaier, Heimo, Spruck, Charles H., Kaiser, Peter, Won, Kwang-Al, Sangfelt, Olle, and Reed, Steven I. Human F-box protein hCdc4 targets Cyclin E for proteolysis and is mutated in a breast cancer cell line. Nature 413, 316-322 (2001).