* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Where is the energy transfer?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
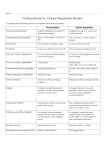
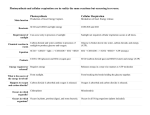
1st Law of Thermodynamics The energy of the universe is constant. Energy can be transformed & transferred, but it cannot be created or destroyed. 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Every energy transfer or transformation makes the universe more disordered. In other words, every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe Based on free energy changes, reactions can be classified as exergonic (energy outward) or endergonic (energy inward). An exergonic reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy. They occur spontaneously. An endergonic reaction is one that absorbs free energy from its surrounds; the energy is stored in the product; they are nonspontaneous. C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy A + B + energy → AB There are many types of biochemical reactions taking place in any living system. Which of the following best characterizes the reaction represented above? A) Catabolism B) Oxidation-reduction C) Exergonic reaction D) Endergonic reaction When you compare the formula for photosynthesis with cellular respiration, which is exergonic, which is endergonic? They are both oxidation/reduction reactions. 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy becomes oxidized C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy becomes reduced 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy CELLULAR RESPIRATION- AN OVERVIEW C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy A molecule that is phosphorylated: a.Has an increased chemical reactivity; it is primed to do cellular work b.Has a decreased chemical reactivity; it is less likely to provide energy for cellular work c.Has been oxidized as a result of a redox reaction involving the gain of inorganic phosphate d.Has been reduced as a result of a redox reaction involving the loss of an inorganic phosphate Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction? C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy a. C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced b. O2 is oxidized and H20 is reduced c. CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized d. C6H12O6 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized Starting with one molecule of glucose, the “net” products of glycolysis are: a.2 NAD+, 2 H+, 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2 H20 b.2 NADH, 2 H+, 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 H20 c.2 FADH2, 2 pyruvate, 4 ATP and 2 H20 d.6 CO2, 6 H20, 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy 1 2 3 5 4 C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Cube Creature A Cube Creature B The length of each small cube is 1 cm. Cube Creature A is made up of 9 cubes. The large Cube Creature is 3cm in length. Cube Creatures take in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide the same way That our cells do. Which Cube Creature is more efficient at gas exchange? A has a 6:1 surface area/volume ratio; B has a 2:1 ratio Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Pyruvate (from glycolysis, 2 molecules per glucose) CO2 NAD+ Glycolysis Citric acid cycle ATP ATP Oxidation phosphorylation CoA NADH + H+ Acetyl CoA CoA CoA Where is the energy transfer? Citric acid cycle FADH2 2 CO2 3 NAD+ 3 NADH + 3 H+ FAD ADP + Pi ATP C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy ATP H H H H H H H H e- H e- e- eH+ e- H+ H+ e- Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy The electron transport chain is a collection of molecules (mostly proteins) embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. The folding of the inner membrane increases the surface area, providing space for thousands of copies of the ETC in each mitochondrion. H Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Add it upSo far only 4 molecules of ATP have been generated HOW MANY SHOULD WE GET FROM THE COMPLETE BREAKDOWN OF A MOLECULE OF GLUCOSE IN THE PRESENCE OF O2? Where is the energy? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Electron Transport Chain- a visualization (my vision) Johnny Depp is my oxygen!!!! Chemiosmosis The energy generated by the ETC is used to pump protons (H+) into the intermembrane space. We have a CONCENTRATION GRADIENT (more H+ in the intermembrane space). All along the inner membrane are protein complexes called ATP synthase. What kind of molecule is ATP synthase? This is the ONLY way that the protons can move back through the membrane. ATP synthase uses the energy of the proton flow to power ATP synthesis. This “coupling” of proton (H+) and ATP synthesis is called chemiosmosis. C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy There is “compartmentalization” within the mitochondrion. What purpose does it serve? How is a concentration gradient important in the process shown here? What is the significance of the inner membrane being folded? Where is the energy transfer? C6H12O6 + 6O26CO2 + 6H20 + energy Add it all up- This is probably 26-28 ATP This number is Probably lower The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? a.Glycolysis b.Accepting electrons at the end of the end of the electron transport chain c.The citric acid cycle d.The oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA Organic molecules besides carbohydrates can transfer energy Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether O2 is present or not and therefore probably evolved first? a.Electron transport b.Glycolysis c.The citric acid cycle d.Oxidative phosphorylation You have a friend who lost 7 kg (about 15 pounds) of fat on a low carb diet. How did the fat leave her body? a. It was released as carbon dioxide and water b. Chemical energy was converted to heat and released c. It was converted to ATP, which weighs less than fat d. It was converted to urine and eliminated from the body Calculate the Gibbs free energy change (G) for the following chemical reaction: ATP ADP + Pi if the reaction occurs at body temperature and the change in heat (H) = 19,070 cal and the change in entropy (S) = 90 cal/oK ΔG = ΔH – TΔS G = Free Energy H = Enthalpy S = Entropy T = Temperature in Kelvin Δ represents change in value over time As far as I’m concerned, they’re the same thing… Photosynthesis !!! Relate the structure to the functionWe have compartmentalization again Lots of surface area Relate structure and function-At the organ level -At the tissue level -At the cellular level -At the organelle level -At the molecular level Photosynthesis- An Overview Where is the energy transfer? Where is the energy transfer? Where is the energy transfer? February 26, 2014 QQ The Light Independent Reactions of Photosynthesis We have a test next week over Unit 7: Energy Transfer Where is the energy transfer? C3 Plants Where is the energy transfer? ΔG = ΔH – TΔS G = Free Energy H = Enthalpy S = Entropy T = Temperature in Kelvin Δ represents change in value over time An experiment determined that when a protein unfolds to its denatured (D) state from the original folded (F) state, the change in Enthalpy is ΔH = H(D) – H(F) = 56,000 joules/mol. Also the change in Entropy is ΔS = S(D) – S(F) = 178 joules/mol. At a temperature of 20⁰C, calculate the change in Free Energy ΔG, in j/mol, when the protein unfolds from its folded state. The correct answer is 3,846 joules/mol. ΔG = ΔH – TΔS ΔG = (56,000 joules/mol) – 293 K (178 joules /mol) ΔG = 56,000 joules/mol – 52,154 joules/mol = 3,846 joules/mol Use these terms to summarize the Calvin Cycle. Carbon dioxide (CO2) Ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) Rubisco 3-phosphoglycerate ATP NADPH Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) Glucose In the Calvin Cycle, CO2 is attached to a molecule of RUBP. This is catalyzed by the enzyme rubisco. The six carbon product splits, forming two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. 3-phosphyglycerate receives a phosphate from ATP and electrons from NADPH forming a molecule of G3P. Two molecules of G3P can combine to form a molecule of glucose. Where is the energy transfer? Photosynthetic Adaptations Alternate mode of carbon fixation that forms a 4-carbon compound as its first product. A way to cut down on photorespiration. Sugarcane, corn, members of the grass family (at least 1000 plants) CAM Photosynthesis Evolved in succulent plants, many cacti, pineapples & other plants. Open stomata during night, close during day Compare and contrast the energy transfer in mitochondria & chloroplas Energy Flow in a Hardwood Forest What percentage of the biomass in the forest community is tied up in the Grass layer which has a question mark? The End