* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Academic Misconduct/ Cheating policy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
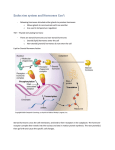
Chapter 11: Reproductive Behaviors Hormones 1. We all know what these are, we talk about them all the time – in reference to what? 2. The technical definition 3. There are two types: 1. 2. Protein hormones – amino acid chains Steroid hormones – carbon rings Steroid Hormones 1. 2. 3. Androgens Estrogens Both are present in both sexes, but differences in activation exist Control of Steroid Release We’ve got two main structures involved in the control of steroid hormones Those hormones go work on other endocrine glands in the system Gonadotropins Gonads What do hormones do? Hormones have two general effects in the body: 1. Organize 2. Activate a) b) primary sex characteristics secondary sex characteristics Nature’s Default… 1. We all start off with the potential to develop into a boy or a girl 2. Activation of a certain region on the Y chromosome (sex-determining region), will cause: 1. 2. 3. The female system (Mullerian) to degenerate The gonads to develop into testes The male system (Wolffian) to develop Sexualization of the Brain 1. During development, it isn’t just the reproductive system that is sexualized, made female or male 2. The hypothalamus is also ‘turned into’ a boy or a girl hypothalamus Sexually dimorphic nucleus Mating Behavior 1. Why do some species have multiple partners and others just one? Where do humans fall on this continuum? 2. The evolutionary perspective 3. However it isn’t just about spreading genes… Issues in Reproduction 1. 2. 3. 4. Difference between genetic sex and gender identity Intersexes Accidents Androgen insensitivity Sexual Orientation There are a number of biological factors that may influence our sexual orientation: 1. 2. 3. Brain differences between homosexuals and heterosexuals Genetic influence Exposure to atypical prenatal hormones