* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 32 - People Server at UNCW
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
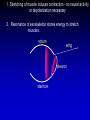
REVIEW AND COMPARISON actin & myosin sarcomeres (banding) t-tubules sarcoplamic reticulum source of Ca2+ speed of contraction spontaneous contraction effect of nerve stimulation stretch prod. contraction skeletal yes yes yes +++ smooth yes no no + cardiac yes yes yes ++ SR SR & ECF SR & ECF fast/slow no very slow yes/no excit. no excit./inhib. yes/no slow yes excit./inhib. yes Cardiac Muscle Autonomic Myogenic Slower contraction Smooth Muscle Parts of two muscle cells Thick and thin filaments interdigitate, but not arranged in sarcomeres Thin filaments anchored to dense bodies Muscle fibers connected by gap junctions Muscle Energetics 5 µmol•g-1 in fiber 100-1000 µmol•g-1•min-1 needed muscle fiber creatine~P arginine~P ATP glycogen glucose glycolysis myosin ATPase • contraction • relaxation SR Ca-ATPase oxidative metab. lactate O2 lipids (amino acids) Although it takes a lot more glucose, ATP can actually be produced faster by glycolysis than by oxidative phosphorylation: Rel. rate Glucose used Lactate prod. oxidative metabolism 36-38 ATP 1 0 glycolysis 64 ATP 32 64 Three types of vertebrate skeletal muscle fibers: Fast glycolytic (white) (FG) Fast oxidative-glycolytic (FOG) Slow oxidative (red) (SO) White and Red Fibers FG FOG SO Speed of contraction fast fast slow Source of ATP glycolysis mixed oxid. met. Myoglobin content low intermed. high # mitochondria few many many # capillaries few intermed. many Glycogen content high intermed. low Lipid content low intermed. high Rate of fatigue fast intermed. slow Skeletal muscles may be a combination of fiber types: e.g. cat soleus - postural muscle - all SO cat gastrocnemius - 45% FG, 25% FOG 25% SO, 5% FG/FOG Different fiber types can be recruited in response to exercise: e.g. gastrocnemius of sprinter - high in FG distance runners - high in FOG + SO Insect flight muscle: Time to relaxation in vert. striated muscle is 5 -10 msec. Some insect wings beat at > 1000 beats • s-1 (midge with wings clipped - 2218 beats • s-1) Must have contraction/relaxation cycle of < 0.45 msec !! - surpasses electrical properties of the membrane Direct or Synchronous Indirect or Asynchronous 1. Stretching of muscle induces contraction - no neural activity or depolarization necessary 2. Resonance of exoskeleton stores energy to stretch muscles: notum wing pleuron sternum