* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Mutations PPT
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
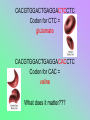
DNA Mutations What if this DNA… CACGTGGACTGAGGACTCCTC …was changed to this DNA? CACGTGGACTGAGGACACCTC What if this DNA… CACGTGGACTGAGGACTCCTC …was changed to this DNA? CACGTGGACTGAGGACACCTC What does it matter??? CACGTGGACTGAGGACTCCTC Codon for CTC = glutamate CACGTGGACTGAGGACACCTC Codon for CAC = valine What does it matter??? Mutation = any change in a DNA sequence - usually happens during DNA replication - in sex cells, it may affect individual’s offspring/children - in body cells, it may affect the individual Mutations can: - be bad, leading to cancer, aging, birth defects, self-aborted embryos - be good, making an organism survive better in its environment - Example: bacteria becoming antibiotic-resistant The ability to drink milk as an adult is a helpful mutation. - have no effect - Example: - CAC = valine - CAT = valine Types of Mutations 1. gene mutations – only affects one gene a. point mutation - a substitution of a single base pair - changes only one amino acid (if any!) Types of Mutations b. frameshift mutation - a single base is added or deleted - changes every amino acid after mutation site - also called a nonsense mutation http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072552980/student_view0/chapter9/animation_quiz_5.html Types of Mutations 2. Chromosomal mutation – may affect more than one gene Examples: nondisjunction, deletion, insertion, inversion, translocation What can cause a mutation? ***A mutation can be inherited, caused by environmental agents, or happen spontaneously Mutagen – anything environmental that can cause a change in DNA Mutagens Radiation – UV, X-rays, nuclear Mutagens Chemicals – asbestos, formaldehyde, chemicals in tobacco products (many mutagens are also carcinogens – cancer causing) Mutation Repair Note: Our DNA mutates all the time, but our cells have repair mechanisms. It is the overexposure to a mutagen that causes the worst problems, because the cell cannot repair all of it in time. Also, repair effectiveness reduces with age. What’s Happening in Japan