* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lh6Ch10Lipids
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Lipopolysaccharide wikipedia , lookup
Cholesterol wikipedia , lookup
High-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
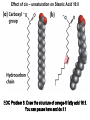
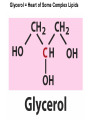
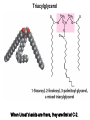
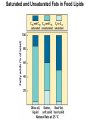
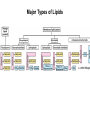
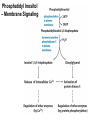
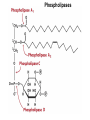
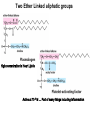
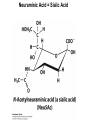
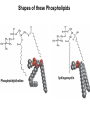
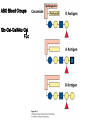
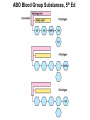
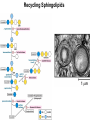
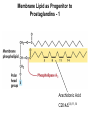
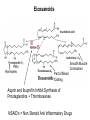
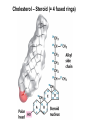
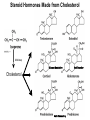
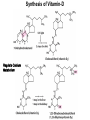
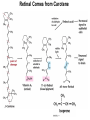
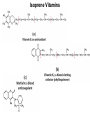
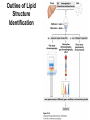
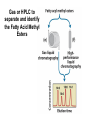
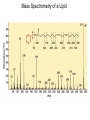
CHAPTER 10 Lipids Lipids Learning Goals: Know: – Biological roles of lipids – Structure and properties of storage lipids – Structure and properties of membrane lipids – Structure and properties of signaling lipids – Methods of Lipid Structure Determination EOC Problem 1 starts off with “what is a lipid” see next slide for the diversity of lipids. Lipids: Structurally Diverse Class Organic molecules that are characterized by low solubility in water, that is, are relatively hydrophobic. Thought question: would some amino acids act like lipids ? …consider I, L, F, W, Y Biological Functions of Lipids • Storage of energy – Reduced compounds: lots of available energy – Hydrophobic nature: good packing • Insulation from environment – Low thermal conductivity – High heat capacity (can “absorb” heat) – Mechanical protection (can absorb shocks) • Water repellant – Hydrophobic nature: keeps surface of the organism dry • Prevents excessive wetting (birds) • Prevents loss of water via evaporation • Buoyancy control and acoustics in marine mammals – Increased density while diving deep helps sinking (just a hypothesis) – Spermaceti organ may focus sound energy: sound stun gun? More Functions • Membrane structure – Main structure of cell membranes • Cofactors for enzymes – Vitamin K: blood clot formation – Coenzyme Q: ATP synthesis in mitochondria • Signaling molecules – – – – Paracrine hormones (act locally) Steroid hormones (act body-wide) Growth factors Vitamins A and D (hormone precursors) • Pigments – Color of tomatoes, carrots, pumpkins, some birds • Antioxidants – Vitamin E Fatty Acid Naming Systems Effect of cis – unsaturation on Stearic Acid 18:0 EOC Problem 8: Draw the structure of omega-6 fatty acid 16:1. You can pause here and do it ! Fatty Acids Go Back to the Table…Look at Melting Points + Their Meaning EOC Problem 2a and 2c Get Into Melting Points and Glycerol = Heart of Some Complex Lipids Triacylglycerol When Unsat’d acids are there, they are first at C-2. Guinea Pig Adipocytes Arabidopsis Seed Section Sperm Whales – Fatheads of the Deep Adjusts buoyancy with Deep dives (1000m deep) by crystallizing and becoming denser…less energy is used by the whale (to overcome buoyancy). Saturated and Unsaturated Fats in Food Lipids Trans Fatty Acids • Trans fatty acids form by partial dehydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids – Done to increase shelf life or stability at high temperature of oils used in cooking (especially deep frying) • A trans double bond allows a given fatty acid to adopt an extended conformation • Trans fatty acids can pack more regularly and show higher melting points than cis forms • Consuming trans fats increases risk of cardiovascular disease – Avoid deep-frying partially hydrogenated vegetable oils – Current trend: reduce trans fats in foods (Wendy’s, KFC) EOC Problem 9: Calalytic hydrogenation of Veggie Oils Wax Ear Wax (Cerumen) is Not Wax The primary components of ear wax are shed layers of skin: 60% of the earwax consisting of keratin 12–20% saturated and unsaturated long-chain fatty acids, alcohols and squalene, 6–9% cholesterol Major Types of Lipids What “X” Can Be: 5th Edition Why are these arrows here? 6th Edition Phosphatidylcholine • Phosphatidylcholine is the major component of most eukaryotic cell membranes • Many prokaryotes, including E. coli, cannot synthesize this lipid; their membranes do not contain phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidyl Inositol – Membrane Signaling Phospholipases Ether Lipids: Plasmalogen • Vinyl ether analog of phosphatidylethanolamine • Common in vertebrate heart tissue • Also found in some protozoa and anaerobic bacteria • Function is not well understood – Resistant to cleavage by common lipases but cleaved by few specific lipases – Increase membrane rigidity? – Sources of signaling lipids? – May be antioxidants? Two Ether Linked aliphatic groups High concentration in Heart Lipids Active at 10-9 M … Part of many things including Inflammation Galactolipids – in Chloroplasts 70-80% of Lipids in Thylakoid Membranes One Type of Achaea Membrane Lipid in Hyperthermophiles Sphingolipids Sphingolipids Discoverer of Sphingolipids Neuraminic Acid = Sialic Acid Shapes of these Phospholipids ABO Blood Groups Glc-Gal-GalNAc-Gal Fuc ABO Blood Group Substances, 5th Ed Recycling Sphingolipids Membrane Lipid as Progenitor to Prostaglandins - 1 Arachidonic Acid C20:4Δ5,8,11,14 Eicosanoids Hormones Part of Blood Clotting Smooth Muscle Contraction Asprin and Ibuprofin Inhibit Synthesis of Prostaglandins + Thromboxanes NSAID’s = Non Steroid Anti Inflammatory Drugs Cholesterol – Steroid (= 4 fused rings) Steroid Hormones Made from Cholesterol Multistep Glucose Metabolism Cholesterol Anti-inflammatory Salt Excretion Synthesis of Vitamin-D Regulate Calcium Metabolism A child who began life in a closet Retinal Comes from Carotene Isoprene Vitamins Mitochondrial and Chloroplast Membrane Electron Carriers Carotenoids Outline of Lipid Structure Identification Saponification and Methylation Gas or HPLC to separate and identify the Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Mass Spectrometry of a Lipid A Little Review Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Fatty acid properties and system of names. 2. Structures of Triacylglycerols. 3. Structures of Glycerol-Phospho-lipids. 4. Structures of Sphingolipids. 5. Progenitor of prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes: arachidonic acid. 6. Cholesterol and other steroids. 7. Analysis of lipids. 8. Know how to do EOC Problems: 1, 2a and c, 7-13 and for fun (if you cook) problem 3 (works the same for Hollandaise sauce).