* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DRUGS for DYSLIPIDEMIAS MED PHARM
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
DRUGS for DYSLIPIDEMIAS
MED PHARM
2/22/2010
DYSLIPIDEMIAS
A MODIFIABLE RISK FACTOR for CV
DISEASE
• LIFESTYLE MODIFICATION WORKS BETTER
THAN DRUGS AND IS CHEAPER
• 1 MG/ML INCREASE LDL-C INCREASES RISK OF
CV DISEASE 2-3%
• 1 MG/ML HDL DECREASE INCREASES CHD
RISK BY 3-4%
An Unstable Arterial Plaque and the Mechanisms of
Plaque Rupture
Heistad D. N Engl J Med 2003;349:2285-2287
FATES OF CHOLESTEROL
Membrane structure
Precursor of steroid hormones and vitamin D
Esterification for storage
Esterification for elimination
Precursor to bile salts
The Basic Components of Cholesterol Synthesis and
Excretion
Nabel E. N Engl J Med 2003;349:60-72
Figure 1. General structure of a lipoprotein.
General Features of Lipoproteins
Apolipoproteins:
specific lipid-binding proteins that attach to the surface
intracellular recognition for exocytosis of nascent particle after synthesis
activation of lipid-processing enzymes in the bloodstream,
binding to cell surface receptors for endocytosis and clearance.
Main lipid components
triacylglycerols
cholesterol esters
phospholipids
Major lipoproteins of the endogenous system:
very low density lipoproteins (VLDL)
intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL)
low density lipoproteins (LDL)
high density lipoproteins (HDL)
Electrophoretic mobility (charge):
HDLs = lipoproteins
LDLs = - lipoproteins
VLDLs = pre- lipoproteins (intermediate between and mobility).
P
100%
C
P
P
Composition
80%
C
P
60%
C
T
40%
C
T
20%
T
T
0%
ChyloVLDL
LDL
microns Lipoprotein Type
HDL
Figure 2. The major classes of lipoproteins and their relative
content of triacylglycerol (T), cholesterol (C) and protein (P).
Summary of Lipoprotein classes:
Lipoprotein
Source
Apo
Protein:Lipid/
Proteins in Major (minor) Lipid
Mature
Transported
Function
VLDL
liver
B100,
CII, E
1:9
triacylglycerol (CE)
Synthesized:
FFA adipose/muscle
CE LDL
IDL
Blood
B100, E
1:3
cholesterol ester
CE liver via apo E
receptor
LDL
blood
B100
1:3
cholesterol ester
CE to liver (70%) and
peripheral cells (30%)
Causal agent in CHD
H
DL
liver
A1, CII, E
("ACE")
1:1
cholesterol ester
supplies apo CII, E to
chylomicrons and VLDL;
mediates reverse
cholesterol transport
OAAmalatepyruvate+NADPH
malic enzyme
Fatty acids oxaloacetate
-oxidation
Citrate
Acetyl CoA
Citrate
Lyase (requires ATP)
(2) Acetyl CoA
+Acetyl CoA
Thiolase
cytoplasm
Acetoacetyl CoA
HMG-CoA
synthase
MITOCHONDRION
HMG CoA
HMG CoA
Statins
reductase
Figure 2. Formation of mevalonate from
HMG-CoA is the rate limiting and
regulated step in the biosynthesis of
cholesterol
Mevalonate
CHOLESTEROL
smooth
endoplasmic
reticulum
Stage 1
Acetyl CoA (C2)
HMG-CoA
NADPH
HMG-CoA
Reductase
NADP+
rate-determining step
cholesterol activates proteolytic degradation
amount controlled by induction/repression
hormonally controlled via phosphorylation
Mevalonate (C6)
Stage 2
Mevalonate
CO2
Active Isoprenoids (C5)
NADPH
Several
Condensation Steps
NADP+
Squalene (C30)
Lanosterol (C30)
Squalene (C30)
3ATP
3ADP
Stage 4
Stage 3
O2
NADPH
NADP+
Cyclization
Squalene
epoxidase/
cyclase
O2
(19 steps)
NADPH
NADP+
Lanosterol (C30)
(4-ring structure)
Figure 3. The four stages of cholesterol biosynthesis
3 CH3
Cholesterol (C27)
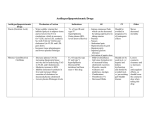
THERAPIES FOR TREATING HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
STATINS
Competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase
Act at low concentration (10-9)
Block HMG-CoA binding site limiting substrate access to catalytic site
Decreased cholesterol synthesis:
in liver = decreased VLDL output and hence LDL production
in all tissues = LDL receptor induction increased LDL uptake
Increase HDL by boosting apo A1 production
Side effects:
liver damage (monitor plasma AST/ALT)
myopathy that can lead to fatal rhabdomyolysis (monitor plasma CK)
negative interactions with other lipid-lowering drugs (fibrates inhibit
statin metabolism)
THERAPIES FOR TREATING HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
BILE ACID SEQUESTERING RESINS
(cholestyramine/colestipol)
Cholesterol is excreted by conversion to bile acids in liver cells
Bile acids are recycled from ileum via enterohepatic circulation to feedback repress 7hydroxylase
Sequestering resins bind bile salts (made from bile acids) to reduce recycling
Chain of events:
reduced recycling lowers liver bile salt concentration
lowers feedback repression
increases hydroxylase activity
increases cholesterol conversion to bile acids
lowers cholesterol concentration
more LDL receptors
increased hepatic uptake of LDL
lowers plasma cholesterol
Side effects:
increases blood triglycerides
abdominal fullness lowers food intake
THERAPIES FOR TREATING HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
NICOTINIC ACID
Water soluble vitamin (niacin; B3)
Increases circulating HDL
May lower circulating LDL
Combined with statin may slow progression of heart disease
Proposed mechanism – decreased release by adipsoe tissue of fatty acids to
lower availability for making TAGs and cholesterol for VLDL
Side effects:
headache, dizziness
long term use linked to liver damage (monitor ALT/AST)
flushing (most common)
THERAPIES FOR TREATING HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
FIBRATES
Improve HDL
Little effect on LDL
Lower circulating triglyceride concentrations
Prescribed in combination with statins
Mechanism unknown
Inhibit the metabolism of statins – Increases
risk of statin myopathy
THERAPIES FOR TREATING HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
EZETIMIBE (ZETIA)
Lowers intestinal absorption of dietary cholesterol
Binds to the Niemann-Pick C1-Like1 (NPC1L1) protein
on epithelial cells
NPC1L1 mediates cholesterol uptake from intestinal
lumen
Side effects: diarrhea, headache, and less commonly
myalgia and liver effects that should be monitored.
STATINS
Actions independent of lipid lowering
•
•
•
•
•
Endothelial function
Coagulation
Vascular inflammation
Smooth muscle
Plaque stability