* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antilipemics
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
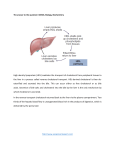
Antilipemics I. Link of cholesterol and CAD-coronary artery disease-Atherosclerotic plaque II. Desired Levels Cholesterol Desired Levels Cholesterol is needed for steroid hormones, cell membranes, bile acids Total Cholesterol <160 Limit fat intake to < 30% of total calories Limit cholesterol to < 300 mg/day Good HDL level F>45 M>55 Can be increased with exercise Bad LDL level CAD <100 No risks <160; 2 risk factors of CHD <130 Triglycerides </=148 Used as fuel by liver to produce cholesterol Form of fat and excess carbohydrates Increases with DM, pancreatitis III. HMG-CoA (Hydroxylmethylglutaryl-Coenzyme A) reductase inhibitors (-statins) *most effective A. AKA: Statins B. MOA: decreases the rate of cholesterol production. Liver requires HMG-CoA to produce cholesterol. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA. When less cholesterol is produced the liver increases the recycling of LDL from the circulation. LDL needed for synthesis of steroids, bile acids, and cell membranes. Metabolized by the liver. Excreted by the kidneys. C. Therapeutic uses: hyperlipidemia D. SE and Adverse Effects: GI, rash, HA, myopathy and rhabdomyolysis; LFTs; dizziness, blurred vision, fatigue, insomnia, myalgias, skin rashes E. Interactions: Statins don’t always play well with others! Digoxin (toxicity) Warfarin ( effect); fibrinic acid or niacin ( risk of rhabdomylosis); macrolide antibiotics; -azole antifungals; grapefruit juice; calcium channel blockers; protease inhibitors (HIV, Hep. C); quinidine, amiodarone, cyclosporine. F. Drug Profiles Lovastatin (Mevacor) Simvastatin (Zocor) Fluvastatin (Lescol Pravastatin (Pravachol) Atorvastatin (Lipitor) F. Contraindications: liver dysfunction and bile acid sequestrants II. Bile Acid Sequestrants A. MOA: bile acids needed for cholesterol; by binding to bile acids removal of LDL from blood ’s. B. Drug Effects: breakdowns cholesterol into bile acids and excreted in fecal matter. C. Therapeutic uses: hyperlipoproteinemia D. SE and Adverse Effects: GI: Constipation, Gas-take with meals E. Interactions 1. Drugs should be take 1 hours before or 4-6 hours after dose 2. absorption of fat-soluble vitamins ADEK F. Drug Profiles Cholestyramine (Questran) Colestipol (Colestid) Colesevelam (WelChol) V. Fibric acid derivatives A. MOA: activate lipoprotein lipase which breaks down cholesterol, inhibits triglyceride synthesis B. Drug Effects: triglyceride levels; HDL; LDL C. SE and Adverse Effects: GI, GU, prolonged PT; LFT; dizziness, HA D. Interactions: anticoagulants, HMG-CoA inhibitors E. Drug Profiles Clofibrate (Atromid-S) Gemfibrozil (Lopid) VI. Niacin; Vitamin B3 A. MOA: believed to inhibit lipolysis in adipose tissue, and increase lipase B. Drug Effects: LDL; triglyceride levels; HDL C. Therapeutic uses: Vitamin supplement needed for bodily processes D. SE and Adverse Effects: Flushing, pruritus, GI distress; vasodilation r/t prostaglandins & histamine (can reduce this by taking NSAIDS and by taking with meals). E. Interactions: with HMG-CoA increase risk of myopathy; Anti-HTN/ B/P F. Drug Profiles Niacin (Niacor, Nicolar) Immediate release (OTC, cheap) SR (Rx, SE) VII. Cholesterol absorption inhibitor A. Ezetimibe (Zetia) B. MOA: prevents cholesterol and related sterols from being absorbed in the small intestine. C. Therapeutic uses: total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides D. Reserved to patients who do not respond to other drugs.