* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
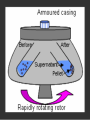
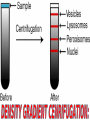
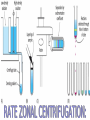
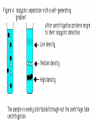
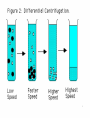
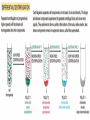
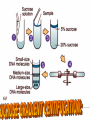
# A mechanical method of seperating immiscible liquids or solids from liquids,by the application of centrifugal force. # It is a piece of equipment,generally driven by an electric motor,that puts an object in rotation around a fixed axis, applying a force perpendicular to the axis. # Isolating suspensions, # Isotope seperation, # Aeronautics & astronautics, # Earthquake & blast stimulation & # Commercial applications. # This technique concerned with the seperation,isolation & purification of subcellular organelles,whole plasma membrane,polysomes,ribosomes,chromatin,nucleic acids, lipoproteins & viruses. # This technique concerned with the study of pure, or virtually pure macromolecules or particles. ROTORS: # Swinging – bucket rotors, # Fixed – angle rotors,& # Vertical rotors. SWINGING – BUCKET ROTORS: FIXED – ANGLE ROTORS: VERTICAL ROTORS: VERTICAL ROTORS: # Density gradient centrifugation, # Rate-zonal seperation, # Isopycnic seperation. # Differential centrifugation, # K – factor centrifugation, # Sucrose gradient centrifugation, # Microcentrifugation, # Superspeed centrifugation,& # ultracentrifugation. # It is useful to purify subcellular organelles & macromolecules. # It is also useful for the determinaton of buoyant densities,& # It is also useful for the estimation of the sedimentation coefficient. 1) Seperation of : # Proteins, # Enzymes, # Hormones, # RNA – DNA hybrids, # Ribosomal subunits,& # Subcellular organelles. 2)For the analysis of size distribution of samples of polysomes & lipoprotein fractionations. # To determine the buoyant density of a particle, # To determine the base composition of the double – stranded DNA, # To separate & purify viruses, # To analyze nucleic acids. centrifugation Sample + Caesium chloride Cscl molecules sedimentation Rise or sediment Concentration gradient (density gradient) Solution density = Own buoyant density It is the most commonly used method,for the isolation of subcellular organelles from the homogenised tissue. # It can be used to determine the time required for pelleting a fraction,with a known sedimentation coefficient. # It is used to purify enveloped viruses & ribosomes. # It will also separate cell organelles from crude cellular extracts. # It will also purify exosomes. # These centrifuges are run in batch to isolate small volumes of biological macromolecules or cells. # It will purify cells & nuclei. # It can be used to isolate subcellular organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum,ribosomes,cytoplasmic components, smaller particles such as proteins & to harvest virus in pure form. # Theodor Svedberg(1925) - Analytical centrifuge # Edward Greydon Pickles - Vacuum centrifuge Pickles(1946) Spinco(1946) Beckman instruments (1954) Model L # It is used for the determination of the macromolecular including amino acid composition of protein,protein’s current conformation, & size distribution of macromolecular samples. They are used in biology for pelleting of fine particulate fractions. # It is the most important widely applied research techniques in biochemistry,cellular & molecular biology, & in medicine.