* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab-Lecture8
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
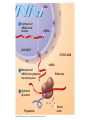
Central Dogma (for your disease?) LB 145 February 22-23, 2011 Deoxyribonucleic Acid Protein (short protein called peptide) • Protein =Amino Acids stuck together • By what kind of bond? • What kind of reaction is this? From Gene to Peptide Functional Peptide: PROTEIN DNA 1 Synthesis of mRNA in the nucleus mRNA NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM DNA 1 Synthesis of mRNA in the nucleus mRNA NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM mRNA 2 Movement of mRNA into cytoplasm via nuclear pore DNA 1 Synthesis of mRNA in the nucleus mRNA NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM mRNA 2 Movement of mRNA into cytoplasm via nuclear pore Ribosome 3 Synthesis of protein Polypeptide Amino acids Cystic Fibrosis is most often caused by mutation DF508 in the CFTR gene o The CFTR gene is 189,000 bases long There are 27 exons/ 26 introns in it. o The mRNA (all exons) is 6129 bases How many codons is that, max? o The protein is 1480 amino acids long Normally it’s a Cl- channel, the mutation? What do you know of your disease’s Central Dogma? o What is the size of your gene? How many exons/introns does it have? o What is the size of your mRNA (cDNA)? How many codons does it have? o What is the size of your protein? What is the normal vs abnormal function of it? Reminders • Peer Review DUE – Might want to look over the criticisms soon-ish • Order your primers by 5pm FRIDAY • Check ATCC.org for cells and DNA.