* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biological Treatment Processes
Sewage sludge wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical oxygen demand wikipedia , lookup
Sewage sludge treatment wikipedia , lookup
Fecal sludge management wikipedia , lookup
Membrane bioreactor wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic lagoon wikipedia , lookup
Constructed wetland wikipedia , lookup
Sewage treatment wikipedia , lookup
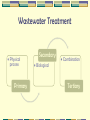
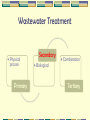
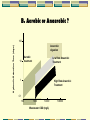
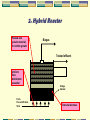
Biological Treatment Processes Outline Overview 3.1 Criteria for Successful Biological Treatment 3.2 Principles of Biological Reactions 3.3Wastewater Treatment Ponds 3.4 Anaerobic Treatment Processes Wastewater Treatment • Physical process Primary Secondary • Combination • Biological Tertiary 2.1 Overview of Treatment Processes Preliminary & Primary Treatment Physical / chemical processes to prepare wastewater for biological treatment Removal of solids mainly Usually cheaper/ easier than secondary processes Examples: a. equalisation (flow and load), b. neutralisation, c. settling of solids, d. flotation of oil and grease, e. filtration etc 2.1 Overview of Treatment Processes Secondary Treatment Biological removal of biodegradable, mostly soluble organic compounds (carbon removal) Aerobically • activated sludge plants, • aerated ponds • trickling filters etc. Anaerobically • non-aerated ponds, • high rate anaerobic (biogas) plants Tertiary Treatment Removal of specific pollutants with physical, chemical and/or biological methods Examples: a. adsorption of organics by activated carbon b. precipitation or flocculation of phosphate etc. c. biological nitrogen removal d. disinfection In general, costs increase with increasing degree of treatment Wastewater Treatment • Physical process Primary Secondary • Combination • Biological Tertiary Outline Overview 3.1 Criteria for Successful Biological Treatment 3.2 Principles of Biological Reactions 3.3Wastewater Treatment Ponds 3.4 Anaerobic Treatment Processes 3.1 Criteria for Successful Biological Treatment Produce biological catalyst (biomass) • source of energy • source of cellular components (C, H, N, O, P, S etc.) Maintain biomass • adequate environment (T, pH, toxics) • adequate retention time (rate of treatment) Separation of biomass • grow suitable types of organisms ie. floc forming bacteria Outline Overview 3.1 Criteria for Successful Biological Treatment 3.2 Principles of Biological Reactions 3.3 Wastewater Treatment Ponds 3.4 Anaerobic Treatment Processes 3.2 Principles of Biological Reactions A. Three Important Biological Reactions Aerobic CHO + O2 biomass + CO2 + H2O ≈ 50 % ≈ 50 % respiratory metabolism Anaerobic CHO biomass + CO2 + CH4 + H20 10 - 20 % 80 - 90 % fermentative metabolism Photosynthesis CO2 + H2O biomass + O2 energy supplied externally (light) B. Aerobic or Anaerobic ? Hydraulic Retention Time (days) 100 Anaerobic digestion 10 Aerobic treatment Low Rate Anaerobic Treatment 1 High Rate Anaerobic Treatment 0.1 100 1000 10000 Wastewater COD (mg/L) 100000 3.2 Principles of Biological Reactions C. Nutrient Requirements "Major" elements: C, H, O, N "Minor" elements: • • • • P DNA/RNA, phospholipids, ATP S for proteins, amino acids K in RNA, coenzymes Mg in RNA, coenzymes, as cation Trace elements • Often essential: Ca, Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn • Rarely essential: B, Na, Al, Si, Cl, V, Cr, Ni, As, Se, Mo, Sn, I Outline Overview 3.1 Criteria for Successful Biological Treatment 3.2 Principles of Biological Reactions 3.3 Wastewater Treatment Ponds 3.4 Anaerobic Treatment Processes 3.4 Wastewater Treatment Ponds Applied mostly in rural industries and small communities Main benefits are low construction and operating cost Classification based on biological activity, form of aeration and influent composition POND TYPE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY TYPE OF AERATION Anaerobic Anaerobic Avoided Facultative (Stabilisation) Anaerobic/ Aerobic Natural Aerated Aerobic Mechanical Aerobic (Maturation, Oxidation) Aerobic Natural 1. Anaerobic Ponds Characteristics: High organic load; Deep (3-6m); Biomass formation small (5-15% of C in feed) Anaerobic Pond Design & Operation Parameter Loading (volumetric) Temperature Mean HRT Unit kg BOD5/m3/d °C Influent COD days mg/L Effluent COD mg/L Operational Considerations: • BOD removal 60-80% • Scum formation to contain odour emissions • Monitor pH (should be 6.4 - 7.8) Typical values 0.1-0.3 25-35 6-25 1000-6000 200-1000 2. Facultative Ponds Characteristics: • “two zone” environment, depth 1.5 - 4 m; large • microbial diversity; medium organic load; odour free Facultative Pond Design & Operation Design: Area Loading Rate • 40 - 140 kg BOD5/ha/d T>15oC • 20 - 40 kg BOD5/ha/d T<15oC • HRT 5 - 30 days Operational Considerations: • Maintain aerobic conditions. Beware of overloading causing the pond to turn anaerobic odour problems 3. Aerated Ponds Characteristics: • Mode is determined by the mixing intensity • Completely mixed: P/V = 2.3 - 4 W/m3 • Facultative: P/V ≈ 0.8 W/m3 Aerated Pond Design & Operation Design: • HRT 0.5 - 3 days • Aeration capacity ≈ 2*BOD load • Aerators: 1 - 1.5 kg O2/kWh • ΔBOD: 50 - 70% Operational Considerations: • Can be very efficient for soluble BOD/ COD removal but solids concentrations too high for discharge (irrigation ok). 4. Aerobic (Oxidation) Ponds Characteristics: • Natural oxygenation (wind, photosynthesis); large surface area; shallow (1 - 1.5m); low organic loading. • Suitable for treating effluent from anaerobic ponds Aerobic Pond Design & Operation Design: 40 - 120 kg BOD5/ha/d Operational Considerations: • Maintain aerobic conditions. Beware of overloading causing the pond to turn anaerobic. Outline Overview 3.1 Criteria for Successful Biological Treatment 3.2 Principles of Biological Reactions 3.3Wastewater Treatment Ponds 3.4 Anaerobic Treatment Processes 3.4 Anaerobic Treatment Processes Treatment under exclusion of oxygen Carbon mainly converted to methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) Used for high organic loadings Efficient and economic COD/BOD removal Low rate systems use very long HRT eg. Anaerobic ponds High rate systems use low HRT but need biomass retention mechanism eg. UASB Increase rate of biological action by increasing temperature. Anaerobic Process Principles Pathways of organics in anaerobic treatment Process types A. Single-stage processes • Long solids & hydraulic retention times (HRT) • Eg. Anaerobic digesters (20-30 d HRT) Anaerobic ponds (10-30 d HRT) B. Two-stage (high rate) processes • Short HRT in first stage, no biomass retention • Short HRT but with biomass retention in second stage, usually pH controlled • Eg. UASB, Hybrid, fluidised bed reactors etc. A. Single Stage Process Biogas SLUDGE DIGESTER Treated effluent Wastewater Mixing mechanically or often by biogas recirculation 1. Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Gas collection below water level to reduce turbulence at overflow Uniform flow distribution essential Biogas Treated effluent Gas collector Sludge blanket From Pre-acidification Tank Granular biomass 2. Hybrid Reactor Packed bed (plastic material) for biofilm growth Biogas Treated effluent Uniform flow distribution essential Sludge blanket From Pre-acidification Tank Granular biomass B. Two-Stage Reactor Performance COD removal 60 - 95% BOD removal 80 - 95% Gas production 0.3-0.6 m3/kg CODremoved Methane production 0.2-0.35 m3/kg CODremoved Methane conc. 55 - 75% Sludge production 0.05-0.1 kg VSS/kgCODremoved Two-stage highrate hybrid reactor for abattoir & industrial wastewater Anaerobic Reactor Design 1. Pre-acidification tank • Often on the basis of an equalisation tank (also variable volume operation) • Typical HRT 12-24 h • pH 5-6 if controlled, 4-5 if uncontrolled • Mixing usually only by inflow importance to minimise solids in influent • Covered tank, gas vented and treated or incinerated (with biogas in boiler or flare) Anaerobic Reactor Design 2. Methanogenic (2nd stage) reactor • Volume-based organic loading rate (OLR) Cin . Q OLR VR Cin biodegradable COD conc. in influent mg/L Q wastewater flow rate m3/d VR methanogenic bioreactor volume m3 Typical HRT 12-24 h, Solids RT 10-150 days Usually heated to operate at 30 - 40°C High Rate Anaerobic Treatment Typical process flowsheet using Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor CSTR-type tank usually not heated Recycle and mix tank reduce pH control dosing Acidif. Tank Mix Tank Acidogenesis Biogas Methanogenesis Sludge blanket Biomass retention as granules Anaerobic Reactor Design OLR designs for various reactor types: • • • • UASB 6-12 kg COD/m3/d Internal Circulation 15-25 kg COD/m3/d Fluidised/expanded bed 12-20 kg COD/m3/d Hybrid Reactor 6-12 kg COD/m3/d OLR varies with degradability, temp., pH… Hydraulic loading up to 24 m3/(m2reactor area d) Gas loading 70 - 200 m3 gas /(m2reactor area d) Questions? Documentation Terima Kasih