* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell: • Small, membrane-enclosed unit • Filled with a concentrated
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
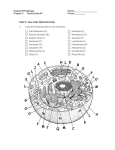
Cell: • Small, membrane-enclosed unit • Filled with a concentrated aqueous solution of chemicals • Ability to create copies of themselves by growing and dividing in two. • The simplest forms of life Feature Size inner membranes skeleton connections Differentiation Semiautomic organelles Procaryiotes 1-10m no 106 circular plasmamembrane dependent no external no no no Apoptosis not sure Nucleus DNA size DNA organization Cell division Eukaryotes 5-100m yes 107-109 linear, histons microtubulusdependent yes internal 3 types yes yes chloroplastis, mitochondria yes Plant and animal cells: Organellum Plant cell Animal cell cellmembrane+wall cellmembrane Plasmamembrane yes Nucleus yes Cytoplasma RER and SER Endoplasmatic Reticulum Free and RER-assotiated Ribosoma ATP production Mitocondrium Golgi apparatus Vacuolum Cytosceleton Synthesis of membrane proteins secretory proteins, polysaccharids Central: water, turgor One or a few: water, ions pressure, similar function to unused compounds animal lisosomes Microtubuli intermedier filaments, microfilaments Organellum Centrosoma Plastis Lisosoma Peroxisoma Plant cell Animal cell no yes yes no rarely yes Fatty acids to glucose helps Protection of the cells from photorespiration free radicals From Golgi Secretory vesuculi flagella rare Cilia yes typical Electronmicroscipic picture of a plant cell http://www.oncoursesystems.com/school/webpage/10845583/788307 Chemical bonds: • covalent bond: it is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons • ionic bond: it is formed when electrons are donated by one atom to another Weak chemical bonds: short-range attractive forces • van der Waals attractions, • electrostatic attractions, • hydrogen bonds: H atom is “sandwiched” between two electron-attracting atoms Chemical composition: Membranes: fatty acids phospholipides, cholesterol: Cell surface compounds, stored nutrients: carbohydrates: monosaccharides, polysaccharides Enzymes, secretory materials, cytosceleton: proteins: amino acids Genome: DNA Protein synthesis, regulation: RNA Energy storage: ATP nucleotide phosphates