* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ester
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
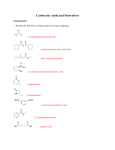
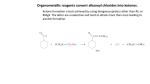
Ester Created And Presented By: Mackenzie Kayler Katie Parry Will Young Kayla Massie Period 7 Basic Structure Esters have a pair of alkyl or aromatic groups connected to a hydrocarbon fragment Ester is created when an acid catalyst is present and carboxylic acids are heated with alcohol. Acid and alcohol react to form water and ester. Characteristics Different types of esters can be created by using different types of acids and alcohol. Esters has very distinctive fruity smells and flavors. Ester is the reason why fruits like bananas, pears, and many others have a smell or taste. Just like the other organic components Ester contains carbon. They are often referred to by their common names. Nomenclature Esters are named based on their carboxylic acids. To name esters, it is easiest to recognize the carboxylic acid and the alcohol the ester is derived from. The first component of an ester name is the alkyl group, which is substituted with an –yl ending. The second component of an ester name is the acyl group, is substituted with an –ate. Nomenclature Practice Mechanism 1 Mechanism of the Base Hydrolysis of Esters This is the reaction of esters with water. By hydrolyzing very complicated esters, we are able to make soap. The reaction with water is very slow, so it is rarely used. Instead, we use a dilute acid so the reaction will happen faster. Mechanism 2 Reaction of LiAIH4 with an Ester By using lithium aluminum hydride, we are able to reduce esters to their primary alcohols. This compound is commonly used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis. Mechanism 3 Reaction of RMgX with an Ester This reaction can also reduce the ester down to its primary alcohol. From using this reactant the alcohol that results contains two identical alkyl groups. Examples Vitamin C- made of Corbate, an internal ester. Vitamin C is a soluble vitamin found in citrus fruits. Isoamyl Acetate- also known as the banana fragrance or oil. The compound is a mixture of amyl pentyl isomers. Benzyl acetate- oil of jasmine. Often used on the skin to heal burns. Methyl Salicylate- Oil of wintergreen. Common in Winto-green lifesavers. Coumarin- found in lavender oil, sweet clover and tonka beans. Real World Importance Aspirin is an ester also known as acetylsalicylic acid. Aspirin is used for prevention of cerebro or stroke. It is manufactured in factories in large quantities It can be used as a analgesic or painkiller. Real World Importance Cont. Millions of people take aspirin everyday. It is often called the “wonder drug” because it reduces pain, fever and swelling. Not only does it lower the risk of heart attack, aspirin has been found to lower the chances of developing cancer. It plays an important role in life because millions of people depend on it as their main pain reliever. For many people, going to the doctors is not an option due to financial reasons or not having health care insurance. Aspirin is an affordable drug that almost guarantees efficiency. Real World Importance Cont. Without aspirin there would be more illnesses and untreated pain throughout the world. Also, there would be more deaths due to cancer, heart attacks, and strokes. Life would be different because people would have to spend more money on other medicines. Also, people would be unhappy with having to use a least effective product. Multiple Choice Questions 1. What does the general structure of an ester look like? A. B. C D. Multiple Choice Questions Cont. 2. What is not an example of an ester? A. Smell of bananas C. Lavender Oil B. Wintergreen Oil D. Smell of wood 3. What kind of odor do esters give off? A. Fruity C. Burned B. Pungent D. No odor Multiple Choice Questions Cont. 4.What does acid connect with to make ester and water? A. Carbon C. Alcohol B. Hydrocarbon D. Ammonium 5. Which is an example of how you would write the name of an ester? A. iron phosphate C. diethyl ether B. methyl propanoate D. dimethylamine Works Cited http://content.onlinejacc.org/cgi/content/full/51/19/1 829 http://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/index_2353/ Notes_Chapter_05.pdf http://faculty.uca.edu/mkelley/2450%20Web%20page s/chapter_15/Some%20Examples%20of%20esters.ht m http://www.chemistry-drills.com/functionalgroups.php?q=simple Http://www.chemguide.co.uk/orgpropsmenu.html Work Cited Cont. http://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicrevie w/bp/2organic/2org_frame.html http://www.ivyrose.co.uk/Chemistry/Organic/Naming-Esters.php http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/351/orgnom/ esters/esters-01.html http://butane.chem.uiuc.edu/cyerkes/Chem104A_BF A05/Genchemref/nomenclature_rules.html http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/carey/stud ent/olc/ch20reactionsesters.html