* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bIOCHEMISTRY - East Pennsboro Area School District
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
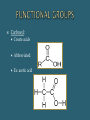
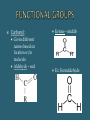
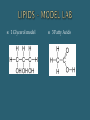
The Chemical Composition of Living Things Four main elements that make up 96% of the human body: Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Hydrogen Inorganic Cmpds: Do NOT contain C Exception to rule CO2 Examples: Water Minerals Metals Sand Rock Carbon molecules Importance of Carbon Forms 4 strong stable covalent bonds Form single, double & triple bonds Polymerization – building of complex molecules Single unit Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Polymer Multiple repeating Examples: Monomer units Macromolecule Large chain of compounds Dehydration Synthesis Hydrolysis Dehydration Loss of water Synthesis Creation Build organic molecules Create bonds = store energy Humans – protein production Plants – fruit & veggie production Hydro – water Lysis – splitting Break organic molecules apart Break bonds = release energy Digestion – release energy from food Molecular Formula Structural Formula # elements in a compound Example: H2 O CH4 C6H12O6 Picture of compound Shows arrangement & bond type Example: H H C H H Must contain Carbon Hydrocarbon: Simplest organic Chains of carbon connected by single, double or triple bonds Remaining bonds are filled with hydrogen Ex: _________ C C C C Ex: _________ C C C C Ex: _________ C C C C Hydroxyl: Also called Alcohols Abbreviated: Ex: Ethanol Carboxyl: Create acids Abbreviated: Ex: acetic acid Carbonyl: Given different names based on location w/in molecule Aldehyde – end Ketone – middle Ex: Formaldehyde Amine: Create bases Abbreviated: Examples: Identifying Organics Is Carbon present? 1. Yes – Organic No - Inorganic Is Nitrogen present? 2. Yes – Protein No – Carb or Lipid Is there a 2:1 ratio of Hydrogen to Oxygen 3. Yes – Carb No - Lipid Monosaccharides Simple sugars Building blocks of carbs Examples Disaccharides Double sugars Created thru dehydration synthesis Examples Glucose – C6H1206 Sucrose – C12H22011 Galactose – C6H1206 Maltose – C12H22011 Fructose - C6H1206 Lactose - C12H22011 Polysaccharides Very long chains of monosaccharides Examples: Functions: Simple – instant Complex – longer lasting Stored energy Starch Plants cellulose Animals glycogen (liver) Cellulose (fiber) Glycogen Chitin Energy Structural Support Cellulose stems & leaves Chitin insect exoskeletons Glucose Fructose Alpha – glucose (Starch) Beta-glucose (Cellulose) Building Blocks Glycerol 3 Fatty Acids Functions: Functions: Long term energy Hibernation Protection Internal organs Insulation Cell membranes Chemical Messengers Surround nerves brain Hormones Saturated Lipids Saturated “full” Hydrogen Carbons of fatty acids all joined by – bonds Found – animals Solid Cholesterol – “bad fat” Unsaturated Lipids Less hydrogen Carbons of fatty acids joined by = bonds Found – plants & fish Liquids Healthier – “good fats” 1 Glycerol model 3 Fatty Acids Amino Acids Building blocks 20 different A. A’s Same basic structure except for “R” group Also called polypeptides Functions: Movement – muscle Transport – blood Protection – immune system Structures – hair, horns, nails, silk, feathers Building blocks – nucleotides Function Store genetic information Create proteins Examples: DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid RNA – ribonucleic acid glycine alanine Terms: Substrate – what is broken down Active site – area where enzyme & substrate connect Lock & Key Theory Extremely specific Unique shape of an enzyme allows it to connect with only 1 substrate Changes to Reaction Rates: Coenzyme - partner (speed up rxn rate) Competitive Inhibitor – substance that blocks the active site & prevent “lock & key” fit (slow rxn rate) Denature - Enzyme loses its shape (slow rxn rate)