* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman civilization From Republic to Empire
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Late Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
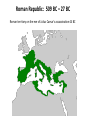
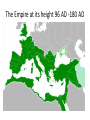
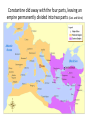
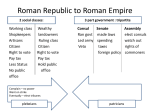
The Roman civilization From Republic to Empire Mr. Dawson Fall 2016 Roman Republic: 509 BC – 27 BC Roman territory on the eve of Julius Caesar's assassination 44 BC Roman Empire: 27 BC – AD 476 o Luke 2:1 “And it came to pass in those days, that there went out a decree from Caesar Augustus, that all the world should be registered.” o Caesar Augustus 27 BC – 14 AD was the first of 170 Emperors! o The last Emperor was 14 year old Romulus Agustulus 475 AD – 476 AD Christianity Question: The Romans were a religious people, in fact they had many gods. What reasons can you think of as to why they initially despised the Christians? The bad emperors • Caligula – 37 AD – 41 AD made his favorite horse a consul and declared himself a god (assassinated) • Nero – 54 AD – 68 AD Had wife and mother murdered, reacted poorly to the great fire in 68 AD (committed suicide after being declared an enemy of the state by the Senate) • Commodus – 180 AD – 192 AD Lazy, encouraged gladiator battles (assassinated) The good emperors 96-180 • • • • • Nerva 96 AD – 98 AD (natural causes) Trajan 98 AD – 117 AD (natural causes) Hadrian 117AD - 138 AD (natural causes) Antoninus Pius 138 AD – 161 AD (natural causes) Marcus Aurelius 161 AD – 180 AD (natural causes) Why are they considered good? • The five good emperors were known for their moderate policies. By contrast their successors were more ruthless and oppressive. This period was particularly notable for its peaceful method of succession. Each emperor chose his successor by adopting an heir. This prevented the civil wars that occurred when other emperors did not chose a successor in advance. This time period came to be known as… Pax Romana (Roman peace) • • • • • Great estates grew Trade flourished Provinces were well governed Peasants prospered The Empire reached its greatest extent, or “height”… The Empire at its height 96 AD -180 AD Diocletian divides the empire in 285 AD into four smaller (and more manageable) parts, however he still had absolute control over the whole empire Constantine the great • Best known for being the first Christian Roman emperor. Constantine reversed the persecutions and encouraged religious tolerance of Christians throughout the empire. • He also is known for moving his capital to the city known at the time as Byzantium. Later, the city would be named Constantinople in his honor. The city is known today as Istanbul, Turkey. Constantine did away with the four parts, leaving an empire permanently divided into two parts (East and West) The Western Roman empire eventually falls to Germanic tribes (like the Goths) in 476 AD How have the Romans “contributed” to cultures of today? Any ideas? Master architects The Arch! Concrete ROMAN Catholic Stadiums Buildings Paved roads Using gravity to get water where needed Latin phrases (language) and Roman numerals The Fall of Rome in the West • No law of succession for the Emperor (power vacuum) • Weak and corrupt leaders • Maintained a large, expensive army • Empire became too large to control ( a few Emperors tried to save the Empire by dividing it in two) • Taxes became too high The end of the Roman Empire in the West The map below (AD 476) shows how the Western Roman Empire lost much of its’ territory while the Eastern part (The Byzantine Empire) didn’t lose any territory A few highlights from the Roman civilization (Republic – Empire) • • • • • • • • 509 BC - Founding of Rome 146 BC – Rome conquers Greece 44 BC – Julius Caesar is assassinated (end of Republic) 27 BC – Caesar Augustus becomes first Roman Emperor 65 AD – Great fire in Rome (Nero is Emperor) 285 AD – Diocletian divides the Empire 313 AD - Constantine declares freedom of religion 476 AD – the last Roman Emperor (Western part) is driven from the throne