* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter Title
Institution of Engineering and Technology wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Anastasios Venetsanopoulos wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
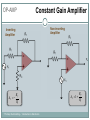
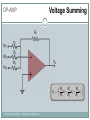
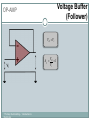
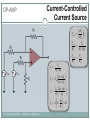
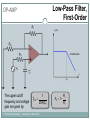
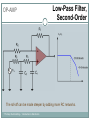
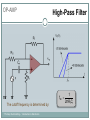
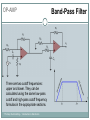
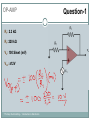
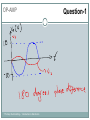
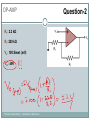
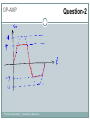
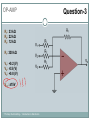
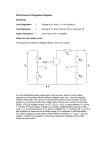
Introduction to Electronics Operational Amplifiers (OP-AMP) CHAPTER 8 Ref: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory Boylestad OP-AMP 1. Constant-gain amplifier 2. Voltage summing 3. Voltage buffer 4. Controlled sources 5. Instrumentation circuits 6. Active filters YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Common Op-Amp Applications OP-AMP Constant Gain Amplifier Non-inverting Amplifier Inverting Amplifier AV Rf R1 YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics AV 1 Rf R1 OP-AMP Voltage Summing R R R Vo f V1 f V2 f V3 R2 R3 R1 YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Voltage Buffer (Follower) OP-AMP VO Vi AV YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics VO 1 Vi OP-AMP Current-Controlled Current Source Rf Vin Vout Rin Vout Vin Rf R1 // R2 Io Vin R1 // R2 R R2 I o Vin 1 R R 1 2 Io Vin R1 R2 R1 R2 R I o I 1 1 kI R2 YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Vout V in Rf Rin Low-Pass Filter, First-Order OP-AMP The upper cutoff frequency and voltage gain are given by: fOH 1 2πR1C1 YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Av 1 Rf R1 OP-AMP Low-Pass Filter, Second-Order The roll-off can be made steeper by adding more RC networks. YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics OP-AMP High-Pass Filter fOL The cutoff frequency is determined by: YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics 1 2πR1C1 OP-AMP There are two cutoff frequencies: upper and lower. They can be calculated using the same low-pass cutoff and high-pass cutoff frequency formulas in the appropriate sections. YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Band-Pass Filter OP-AMP R1: 2.2 kΩ Rf: 220 kΩ Vs: 100 Sinwt (mV) Vcc: ±12V YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Question-1 OP-AMP YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Question-1 OP-AMP R1: 2.2 kΩ Rf: 220 kΩ Vs: 100 Sinwt (mV) Vcc: ±9V YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Question-2 OP-AMP YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Question-2 OP-AMP R1: 33 kΩ R2: 22 kΩ R3: 12 kΩ Rf: 330 kΩ V1: +0.2 (V) V2: -0.5 (V) V3: +0.8 (V) Vcc: ±15V YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Question-3 OP-AMP YTU-Dep. Electrical Eng. / Introduction to Electronics Question-3