* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rad T 110
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
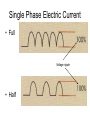
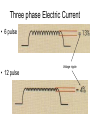
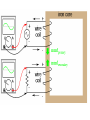
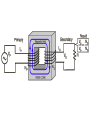
Rad T 110 Electromagnetic Radiation The Wave Equation • Velocity = frequency x wavelength – Remember, photons all travel at the speed of light, 186,000 miles/second so velocity is in effect a constant • Consequently, any changes to either frequency or wavelength have to be accompanied by a change in the other. • So, if frequency increases then wavelength decreases. • Conversely, if frequency decreases then wavelength increases. What is frequency? • Frequency is defined as the number of wave forms per second. • In the case of x-ray photons about 1019 cycles per second. • Frequency is a representation of energy. • As beam energy is increased, frequency increases. Beam Energy • Beam energy is determined by kVp. • Therefore, the higher the kVp the higher the photon frequency. • The higher the kVp – The higher the beam quality – The harder the beam – The higher the penetrability of the beam Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave-particle Duality • Higher energy photons act like particles. • Low energy photons act like waves. Inverse Square Law • Addresses the issue of the divergent beam. • As the beam travels it diverges or spreads out. The further it travels the more spread out it becomes. • However, given that the same number of photons are in the beam their concentration or intensity will be diminished. Single Phase Electric Current • Full Voltage ripple • Half Three phase Electric Current • 6 pulse Voltage ripple • 12 pulse Electromagnetic Induction • Faraday’s Law – An electric current is induced in a circuit if part of the circuit is in a changing (alternating) magnetic field. – Also, a magnetic field can be generated by alternating magnetic fields. Transformers and Mutual Induction • Transformers work with AC current through the application of Faraday’s Law. – An AC electric current induces a varying magnetic field in a piece of iron (electromagnet). – Another piece of wire is wrapped around the iron. In this wire an electric current is induced. Why, because the magnet field is moving throughout the iron. – So, without an AC current you would not induce a varying magnetic field. Step-down transformers • These transformers also work on the principle of mutual induction; however, their goal is to decrease the incoming voltage. • So, the secondary side has fewer windings than the primary side. • Any device you have at home that runs on batteries and AC has a step-down transformer. It is usually the little black box that gets hot. Step Up Transformers • These transformers are intended to increase voltage. • Remember, incoming voltage is relatively low (<480 V) is in order to create kVp you are going to have to dramatically increase the voltage. • This is done by having more wires on the secondary side of the transformer than the primary side. • The primary side of the transformer is were the voltage comes in. • The step-up transformer can also be called a highvoltage or hightension transformer. Closed core transformer Types of Transformers in X-ray Circuits • Autotransformer – Has only one winding and works on the principle of self-induction (because of the single winding). • Step-up transformer, high voltage or high tension • Step-down or filament transformer – Both of these are generally shell type transformers and work using mutual induction.