* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformer
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
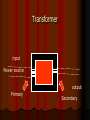
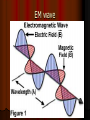
Transformer ~can either “step up” or “step down” the voltage provided to it. i.e. with the appropriate transformers you could make a 12 V current 24 V or 6 v. Or 120 V can be 6 V It is created by wrapping two different wires around the same conductor Transformer input Power source output Primary Secondary How a transformer works The change is caused by the number of loops (turns) on the primary and secondary. Assume both have 1 turn (loop), and the primary is a 12 V source then the primary would induce a magnetic field in the conductor, which will induce an electric current in the secondary with 12 V Now transforming If the primary 1 V has one turn and the secondary has two turns, then each loop will get a 1 V, so it will have a total of 2 V. If the primary 2 V has two turns and the secondary has one turn, the secondary will have 1 V. One of the major reasons AC is used as the primary power source is the ease in stepping up or stepping down the voltage as needed Step up transformer input Power source output Primary Secondary Equation Primary voltage = Secondary voltage # of primary turns # of secondary turns If the power in the lines is 120 V with 20 turns going into a transformer with 10 turns what will the voltage be? V1 / T1 = V2 / T2 120/ 20 = V2 / 10 =60 V Power line transmission To transfer electricity across long distances you have to use extremely high voltage (like 120,000 V) and low current Otherwise you lose a lot of energy due to heating of the wire Transformers easily step down the voltage to 120 V used in our homes, or up to a good amount to transfer it Electromagnetic Radiation electromagnetic induction occurs without a wire for the current to travel through. Moving any charged object (like a balloon rubbed on your head) will create… A moving magnetic field which in turn will create… A moving electric field which causes… This continuously repeats This wave moves through space. EM wave Electromagnetic waves Since the waves travel due to a constant electromagnetic induction they always travel at the same speed. This speed is exceptionally fast, as a matter of fact it is the fastest anything can ever go This speed is…. 3.0 x 108 m/s in a vacuum. homework Pg 758 11-16; 19-22