* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download P3.3 keeping things moving checklist File
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
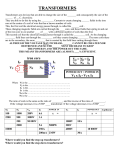
P3.3 Keeping things moving Can you…? P3.3.1 The motor effect State that a magnetic field is produced around a wire when a current flows through it Give examples of applications of electromagnets, such as cranes for lifting iron/steel Describe the principle of the motor effect and its use in any given situation Outline how the motor effect creates movement in electric motors Explain two ways that the size of the force can be increased State that a conductor will not experience a force if its is parallel to the magnetic field Identify the direction of the force using Fleming’s left-hand rule State that the direction of the force is reversed if either the direction of the current or the direction of the magnetic field is reversed Interpret diagrams of electromagnetic appliances in order to explain how they work P3.3.2 Transformers Describe how a potential difference is induced across the ends of an electrical conductor when it ‘cuts’ through a magnetic field Describe how a potential difference is induced across the ends of a coil if a magnet is moved into a coil of wire Outline the basic structure of a transformer Outline how an alternating current in the primary coil produces a changing magnetic field in the iron core and hence in the secondary coil, which in turn induces an alternating potential difference across the ends of the secondary coil Compare the potential difference across the primary and secondary coils in stepup and in step-down transformers Relate the potential difference across the primary p p and secondary coils of a transformer using the equation: s s Relate electrical power input and output for p s s p tranformers, assuming they are 100% efficient, using the equation: State that switch mode transformers operate at a high frequency, often between 50 kHz and 200 kHz Explain the advantages of switch mode transformers working from a 50 Hz mains supply in terms of size and weight, and why this makes them useful for applications such as mobile phone chargers State that switch mode transformers use very little power when they are switched on but no load is applied Compare the use of different types of transformer for a particular application. Examples might include mobile phones chargers and power supplies for laptops V n V n V I V I