* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Engineering Review – Electric Circuits I
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
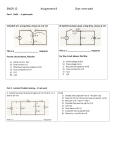
OHMS LAW V = Voltage, I = Currect, R = Resistance of in a circuit V=I*R Power: 𝑽𝟐 𝑷𝒐𝒘𝒆𝒓 = 𝑰 ∗ 𝑽 = = 𝑰𝟐 ∗ 𝑹 𝑹 RESISTORS • Combining resistances in series: 𝑹𝒆𝒒 = 𝑹𝟏 + 𝑹𝟐 … + 𝑹𝒏 • Combining resistances in parallel: 𝑹𝒆𝒒 = 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 + +⋯ 𝑹𝟏 𝑹𝟐 𝑹𝒏 CAPACITORS • Combining capacitors in series: • 𝑪𝒆𝒒 = • Combining capacitors in parallel: 𝑪𝒆𝒒 = 𝑪𝟏 + 𝑪𝟐 … + 𝑪𝒏 • Charge on a capacitor: 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 + +⋯ 𝑪𝟏 𝑪𝟐 𝑪𝒏 Charge = Q =C*V C = Capacitance, V = Voltage Across the capacitor INDUCTORS • Inductors in series: 𝑳𝒆𝒒 = 𝑳𝟏 + 𝑳𝟐 + ⋯ 𝑳𝒏 • Inductors in parrellel: 𝑳𝒆𝒒 = 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 + +⋯ 𝑳𝟏 𝑳𝟐 𝑳𝒏 KIRCHOFF’S CURRENT LAW (FOR NODES) 𝑰𝒊𝒏 = • 𝑰𝒐𝒖𝒕 This can be applied to a node to determine the current in a leg of the other legs are know, by summing the currents in and out of the node. KIRCHOFF’S VOLTAGE LAW 𝑽𝒓𝒊𝒔𝒆𝒔 = • 𝑽𝒅𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒔 This means that in any loop of a circuit, the sum of the voltage sources is equal to the voltage drops caused by the loads.