* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Circuits
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
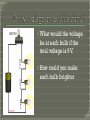
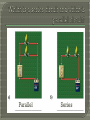
Chapter 20.3 Key Concepts: • What is included in a circuit diagram? • How do series and parallel circuits differ? • How do you calculate electric power and electrical energy used? Vocabulary: • Electric circuit • Series circuit • Parallel circuit • Electric power Use symbols to represent parts of a circuit. Include: • Sources of electrical energy • Devices that are run by electrical energy Each battery = 1.5V Charge has only ONE path through which it can flow. If one element stops functioning in a series circuit, NONE of the elements can operate. • The bulbs in a circuit are a source of resistance. The more bulbs, the more resistance. Voltage is split equally among the resistors in the circuit. + 6V 3V - Current is the same throughout the circuit. 0V What would the voltage be at each bulb if the total voltage is 9 V. How could you make each bulb brighter Charge has TWO OR MORE paths through which the charge can flow. If one element stops functioning, the rest of the elements can still operate. Parallel Series Power is the rate of doing work. • Power is measured in WATTS (W). Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is converted to another form of energy. Electrical power is calculated by multiplying voltage by current. P (watts) = I (amps) x V (volts) Electrical power is calculated by multiplying voltage by current. Power (P) = Current (I) x Voltage (V) (W)atts (A)mps (V)olts An electrical oven is connected to a 240volt line, and it uses 34 amps of current. What is the power used by the oven? P = I xV P = 34A x 240 V P = 8200 W Math Practice • Page 611 Problems 1 – 3 • Page 613 Problem 7 - 8 How much energy is used by an appliance. • Energy = Power x Time •E=Pxt • Unit = kilowatt-hours