* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06. Questions of Values and Ethics
Philosophy of healthcare wikipedia , lookup
Moral disengagement wikipedia , lookup
Cosmopolitanism wikipedia , lookup
Individualism wikipedia , lookup
Value (ethics) wikipedia , lookup
Moral relativism wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Bernard Williams wikipedia , lookup
Virtue ethics wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
Kantian ethics wikipedia , lookup
APA Ethics Code wikipedia , lookup
J. Baird Callicott wikipedia , lookup
Nel Noddings wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Hill Green wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of eating meat wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethics wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian ethics wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
Secular morality wikipedia , lookup
Primary care ethics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
Declaration of Helsinki wikipedia , lookup
Compliance and ethics program wikipedia , lookup
Medical ethics wikipedia , lookup
Clare Palmer wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Arthur Schafer wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of technology wikipedia , lookup
Jewish ethics wikipedia , lookup
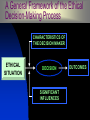
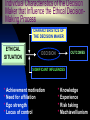
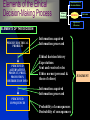
Questions of Values and Ethics Values Abstract ideals that shape an individual’s thinking and behavior – a moral compass Instrumental values – certain way of behaving is appropriate in all situations – “means”. Terminal values – enduring belief in the attainment of a certain end state – “ends”. A moral compass These abstract ideals can result from Religion Philosophy Family teachings Instrumental values As the means to an end they become the ingrained ways of behavior: Rituals Politesse Good habits Terminal values With the end always in sight: Heaven Respect Financial Success Personal Independence Power Ethics The study of moral obligation involving the distinction between right and wrong. Business Ethics: right or wrong in the workplace – value management. Relativism Egoism The 4 Concepts of Ethics Utilitarianism Universalism ETHICS THEORY/THEORISTS “Ethicists” Ethical Tests Is It Legal Test? Ethical Quadrant II Ethical and Illegal Illegal Quadrant I Codification Ethical and Legal Manifestation Corporate Legal Decisions Quadrant IV Quadrant III Unethical and Illegal Unethical and Legal Unethical Two Areas of Business Ethics Obvious mischief Moral mazes RIGHT vs. RIGHT Common Misconduct in Organizations Misrepresenting hours worked Employees lying to supervisors Management lying to employees, customers, vendors or the public Misuse of organizational assets Lying on reports/falsifying records Sexual harassment Stealing/theft Accepting or giving bribes or kickbacks Withholding needed information from employees, customers, vendors or public Common Causes of Unethical Behavior Pressure Fear Greed Convenience Causes of Unethical Behavior (cont’d) Following boss’s directives Meeting overly aggressive business/financial objectives Helping the organization survive Meeting schedule pressures Be a team player (group think) Rationalizing that others do it Resisting competitive threats Advancing own career Ethical Dilemmas Making decisions under stress or dealing with complex issues that have no clear indication of what is right or wrong. There are NO simple ethical dilemmas… all have layers of meaning and effect. Business Ethics Myths Business ethics is a new fad. Business ethics – religion vs. management. Business ethics is obvious – “do good!” Business ethics is good guys preaching to bad guys. “Whistleblower’s” Reluctance Didn’t believe action would be taken. Feared retaliation from mgmt. Didn’t trust confidentiality. Feared not being a team player. Feared retaliation from co-workers. Didn’t know who to contact. Nobody cares, why should I? Business Ethics Myths (cont’d) Ethics can’t be managed. Being legal = being ethical. Managing ethics has little practical relevance. Ethical Tips for Organizations Develop a code of ethics. Communicate code and bake it into culture top-down. Treat ethics as a process. Create open lines of communication. Set good examples. Educate employees – frame issues through storytelling. Value forgiveness. Benefits of Managing Ethics in the Workplace Improves society. Maintains a moral course in turbulent times. Cultivates employee teamwork, productivity, morale and development. Acts as an insurance policy. Benefits of Managing Ethics in the Workplace (cont’d) Establishes values for quality management, strategic planning and diversity management. Promotes strong public image. It is the RIGHT thing to do! Ethical Tips for Individuals Establish personal values. Be aware of ethical events. Develop critical thinking techniques. Be reflective. Make it a priority every day. “The simple step of a simple courageous man is to not take part in the lie, not to support deceit. Let the lie come into the world, even dominate the world, but not through me.” -- Alexander Solzhenitsyn Puzzling things out…. As we watch the video vignettes, keep these questions in mind: 1) What is the ethical dilemma? 2) What is the apparent cause of the unethical behavior? 3) Is there an ethical resolution to the problem portrayed? 4) If so, who should do what? Decision-Making Process A General Framework of the Ethical Decision-Making Process CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DECISION MAKER ETHICAL SITUATION DECISION SIGNIFICANT INFLUENCES OUTCOMES Individual Characteristics of the Decision Maker that Influence the Ethical DecisionMaking Process CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DECISION MAKER ETHICAL SITUATION OUTCOMES DECISION SIGNIFICANT INFLUENCES * Achievement motivation * Need for affiliation * Ego strength * Locus of control * Knowledge * Experience * Risk taking * Machiavellianism Significant Influences on the Ethical Decision-Making Process CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DECISION MAKER ETHICAL SITUATION DECISION OUTCOMES SIGNIFICANT INFLUENCES * The organization * Work * The law * Economics * Professionalism * Technology * Significant others; customers, peers, immediate supervisor, top managers, family, friends, other “opinion leaders” Outcomes that Result from the Ethical Decision-Making Process CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DECISION MAKER ETHICAL SITUATION DECISION OUTCOMES SIGNIFICANT INFLUENCES * Performance * Rewards * Satisfaction * Feedback * Promotions * Learning Elements of the Ethical Decision-Making Process Characteristics of Decision Makers Ethical Situation DECISION Outcomes Significant Influences ELEMENTS OF THE DECISION PERCEIVED ETHICAL PROBLEM PERCEIVED ALTERNATIVES, PRODUCT, PRICE, PROMOTION, DISTRIBUTION INFO Information acquired Information processed Ethical decision history Expectations Sent and received roles Ethics norms (personal & those of others) Information acquired Information processed PERCEIVED CONSQUENCES Probability of consequences Desirability of consequences JUDGMENT A Successful Code of Ethics • Have support of top management • Be practical and realistic • Followed by top management • Include penalties for disobedience • Clearly explained to all employees • Continuously implemented by a "watchdog committee" that has authority to take disciplinary actions Human Resources (HR) International Affairs Research & Development (R&D) Accounting Inside an Organization: How ethics affects the everyone! Information Technology (IT) Production Sales/Marketing Ethics of Accounting Creative accounting practices and misleading financial analysis. White-collar crimes Executive compensation Bribery, kickbacks, political lobbying Ethics of Sales and Marketing Pricing: price fixing, discrimination, skimming. Unethical marketing strategies Content of Advertisements Children and marketing Black and grey markets. Ethics of Production Defective products Quality vs. Quantity Addictive and inherently dangerous products and services (e.g. tobacco, alcohol, weapons, motor vehicles, chemical manufacturing). Environmental issues Safety Patent infringement Ethics of Research & Development (R&D) Ethical problems arising out of new technologies: genetically modified food, mobile phone radiation and health. Product testing ethics: animal rights and animal testing. Use of economically disadvantaged groups (such as students) as test objects. Intellectual property Ethics of International Business Political Economic Socio-cultural Technological Legal Environment Government