* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANTS
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
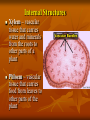
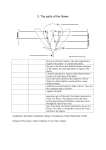
PLANTS The plant kingdom is divided into both non-vascular and vascular plants. All plants are eukaryotic, multi-cellular, and non-mobile. Flowering plants AKA Angiosperms Have specialized reproductive organs called flowers Within the flower are the MALE stamen FEMALE pistil In A Vascular Plant… 1. Leaves A: Functions a. Makes and stores food for the plant b. site of gas exchange like Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide 1. Leaves… continued c. Respiration d. Photosynthesis B. Tissues of the Leaf: a. Cuticle: waxy substance that covers the leaves and stems. Waterproof layer that keeps water in plants b. Stomata: openings mainly located on the underside of leaves. Helps with exchange of gas c. Vascular tissues: called vessels. Examples are xylem and phloem. 2. Stem A. Functions a. b. c. d. e. movement of materials (through xylem and phloem) Support flower & reproductive structures Food storage Xylem: the tissue that transports water & nutrients UP from roots to stems and leaves Phloem: tissue that transports food DOWN from leaves to roots Stem – carries substances between the plant’s roots and leaves; provides support for the plant and holds up the leaves so they are exposed to the sun. Internal Structures Xylem – vascular tissue that carries water and minerals from the roots to other parts of a plant Phloem – vascular tissue that carries food from leaves to other parts of the plant 3. Roots A. Functions: a. b. c. d. Anchors the plant Absorbs water & minerals Store food (starches) Can also support some plants External Structures Roots – a structure that anchors a plant in the ground, absorbs water and minerals from the soil and sometimes stores food in the form of starch. 4. Flower A. a. b. c. Function Contains the reproductive organs for the plant Produces fruit, which protects, nourishes and carries seeds Attracts insects for pollination Flower Continued B. Parts of the Flower a. sepal: outer covering of the flower bud that protects the stamens and pistils when flower is in the bud stage b. Petals: brightly colored, protects stamen & pistils, attracts pollinating insects c. Stamen (male): i. anther: produces pollen (sperm) ii. Filament: supports the anther d. Pistil (female): i. ovary: enlarged portion at base of pistil, Produces eggs/ovules which develop into seeds ii. Stigma: holds the pollen grain iii. Style: Connects the stigma with the ovary, holds the stigma so that it cam be pollinated Parts of a Flower Sepal – leaflike structures that protect the developing flower and are often green Petals – a colorful, leaflike structure of some flowers Stamen Made of filament that holds up anther The anther produces the pollen Pistil Has a sticky stigma Held up by the style The style connects the stigma to the ovary The ovary contains the eggs Pollination Pollen sticks to the stigma and falls down the style to the ovary The eggs are fertilized and become seeds Then the ovary turns into a fruit. Germination Seed plants go through a variety of developmental stages Beginining with germination of the seed The seed contains the young plant and stored food Germination requires water Non-Vascular plants… Are low growing Do not have roots Obtain water and materials directly from their environment or nearby cells Transpiration – the process by which water evaporates from a plant’s leaf