* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angiosperm Anatomy Slideshow
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
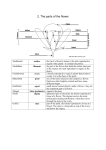
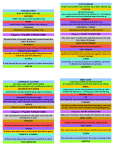
ANGIOSPERM ANATOMY Colwyn Sleep Strawberry Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Subkingdom: Tracheobionta Division: Magnoliophyta Class: Magnoliopsida Subclass: Rosidae Order: Rosales Family: Rosaceae Genus: Fragaria Species: Fragaria ananassa PARTS OF ANGIOSPERM Leaf Flower Stem Fruit (mature ovary) Carpel (stigma, style, and ovary) Stamen (anther and filament) Petal Root System Stigma ROOT SYSTEM Roots Plant and Root -absorbs water and nutrients -anchors the plant to the ground -stores food and nutrients Main Root Lateral Root Tap Root STEM Stem -supports and elevates the leaves, flowers and fruits. -keeps the leaves in the light and provides a place for the plant to keep its flowers and fruits. -transports fluids between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem. LEAF -Conducts Photosynthesis (Chlorophyll in leaves uses the energy in sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide gas into sugar and oxygen gas) Stomata in leaf controls the intake of carbon dioxide Veinous leaf structure FLOWER Flower petals grow in groups of 8 Petal shape and colour helps to attract pollinators Petal Sepal -Protects the flower during its bud stage MALE REPRODUCTIVE STRUCTURE Stamen -male reproductive structure Anther produces the male gametophyte “pollen” Filament -supports and holds the anther FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE STRUCTURE Carpel -female reproductive structure Stigma Style -sticky tip of the style that catches and holds pollen -supports the stigma -location where pollen tube forms Ovary -protects the ovule Ovule -Produces egg Receptacle where flower organs grow DEVELOPING FRUIT Remaining Stamen Early seed development The mature ovary forms a fruit which is eaten and aids in seed dispersal MATURE OVARY Strawberry Seeds -germinate and begin the next generation Mature Fruit -acts as food so the fruit is consumed and dispersed -provides food for the seed as it grows -protects the seed DICOT CLASSIFICATION Flower Petals grow in groups of 8 Leaf has venous structure Roots are tap-root style