* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS (Flowering Seed Plants
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
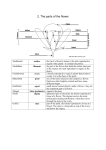
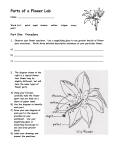
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS (Flowering Seed Plants are called __________________) 1. Most flowers have four parts: ____________, ___________, ______________ (male part) and _____________ (female part). 2. a. Sepals protect the _________________until it opens. b. Petals attract ______________________________. c. Stamens make_______________________________. d. Ovary grows into fruits which contain the _______________. 3. Stamen: Is made up of the ____________ which holds the ____________ grains. The _______________ holds the _______________ up. 4. Pistil: Contains the _____________, _______________, _______________ and _________________(eggs). sepal - the sepals are small leaves located directly under a flower anther - the anther is the tip of a flower's they are the outermost part of a flower. stamen ( the male reproductive organs of the stem (also called the peduncle) - the stem supports the plant. plant) - it contains the pollen. filament - the filament is the part of the flower stigma - the stigma is uppermost part of the pistil, the female reproductive tissue of a flower. The stigma receives the male pollen that holds the anther (and part of the stamen, grains during fertilization, when they travel through the style to the the male reproductive organs of the plant). ovary - Be the ovary a female reproductive organ stamen, ovary. ableis to label the pistil, petals, sepals, anther, filament, in plants that produces ovules. It is at the base style - the style is part of the pistil, the female reproductive tissue stigma, style, ovary andisovules. of the pistil. of a flower. The style a long tube on top of the ovary, and below petal - a petal is one of the leafy structures that the stigma. comprise a flower. Petals are often brightlyOvule – plant structure that develops into a seed when it is colored and have many different shapes. fertilized (located inside the ovary) 5. Flowering plants use the _________, _____________, ____________, ____________ and ________________ to transfer pollen from the male (stamen) part of the flower to the female (pistil) part of the flower. 6. A flower is pollinated when a pollen grain lands on its ________. 7. In fertilization, pollen grains move from the stigma, down the _____________ to reach the ____________. 8. Fertilized ovules develop into ________________. The ____________ enlarges to form the flesh of the _____________________ and to protect the ovules (seeds). 9. Seeds are dispersed in many different ways: _________, __________, and animals which might include _____________, ____________ or ____________. 10. How do birds and animals help with seed dispersal?__________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ Non-Flowering Seed Plants are called ___________________. Chart comparing gymnosperms and angiosperms. Gymnosperms Bare seeds Seed inside fruit Flowering Plant Produce Cones Produce Fruit Wind Pollinates Insects Pollinate Angiosperms