* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2-fossils and rock dating
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
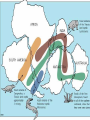
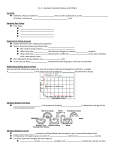
Fossils: are the remains of animals, plants or humans found in sediments and rocks. e.g. bones, shell, leaves, carapace. Fossilization: transformation of a living organism into a fossil. This is a very long process. • The process of fossilization: – The animal, plant or human dies – Soft tissues (muscles and organs) are eaten or decomposed – The hard parts (skeleton) are covered with sediment – Over years, the sediments harden into rocks. – The fossils are found by scientists…or you! • Fossilization of a dinosaur: • What do fossils teach us? – A) the different forms of life that have existed on Earth. – B) the changes that have marked Earth’s history • Tectonic plates have changed Earth’s appearance and that is why similar fossils are found on different continents far away from each other. • Stratigraphy: sediments deposited on ocean floor, form rocks over time and are usually arranged in layers. • Every stratigraphic layer is composed of sedimentary deposits of the same color, size and type of rock. • The oldest layer is always on the bottom with the youngest layer on the very top. This is the principle of superposition. – E.g. old vs. new newspaper in the recycling bin. • Dating fossils: – There are two methods of dating fossils • Relative dating: determining the age of fossils and rocks by examining their location in the superpositioned layers. • Absolute dating: determining the age of fossils and rocks by measuring the quantity of certain radioactive elements (uranium and carbon 14) in the specimen. • Index fossils: are fossils that help scientists find the approximate age of layered sediments. • E.g. Scientists know the age of ammonites, a marine animal. When ammonites are found in rock layers, scientists know that the rock is approximately 110 Ma because that is the age of the ammonite found within.