* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download All About Plants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
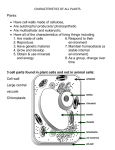
All About Plants What is a Plant? • • • • • An autotroph A producer A multicellular eukaryote Perform photosynthesis Includes trees, shrubs, grasses, mosses, and ferns. • Aquatic and terrestial • Over 270,000 species identified • THEY ARE ALIVE!!!!! What a Plant Needs to Survive • • • • Sunlight Water and Minerals Gas Exchange Movement of Water & Nutrients Plant Life Cycle • • • • • Plants have two alternating phases, a (2N) dipoid phase and an (N) haploid phase. 2N is the sporophyte N is the gametophyte The haploid gametophyte stage produces eggs & sperm The diploid sporophyte stage produces spores Types of Plants 1. Nonvascular Plants • Mosses, liverworts, hornworts 2. Vascular Plants • Seedless • • Clubmosses, horsetails, ferns Seed • Gymnosperms • • Conifers Angiosperms • Flowering Plants Nonvascular Plants - Bryophytes Liverworts Seedless Vascular Plants Clubmoss Ferns Horsetails Seed Plants -- Gymnosperms • Cone-bearers cycads Ginkgoes Seed Plants -- Angiosperms Stinking corpse lilly Plant Tissue Systems • Dermal Tissue • The skin of the plant. The outmost layer of cells. Waxy layer helps the protect against water loss. • Vascular Tissue • Transport system that moves water and nutrients throughout the plant. • Ground Tissue • Cells that lie between the dermal and vascular tissue. • In leaves these cells are packed with chloroplasts and are the site of photosynthesis. Roots • • • • • • Anchors plant Absorbs water & nutrients Growth occurs at the apical meristem Root cap protects apical meristem Root hairs help absorb water and minerals and increase the surface area of the root The core of the root is called the vascular cylinder & contains xylem & phloem Taproots vs fibrous roots Taproots grow deep to reach water. Taproots may store food (carrots & beets). Fibrous roots grow near the surface and spread out to collect water. Fibrous roots like in grasses help prevent erosion. Stems • Stems produce leaves, branches, and flowers • Stems hold leaves up to the sunlight • Stems transport substances between roots and leaves • Xylem and phloem form continuous tubes from the roots through the stems to the leaves Woody Stems Monot vs. Dicot Monocot Dicot Vascular bundles scattered throughout the stem Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring • • • Dendrochronology (Tree Time) Tree rings tell how wet or dry the growing seasons were, when a fire swept through the area, or when damage occurred. Each ring has two colors: the light color is the wet season growth and the dark color is the cold or dry season growth. If the light color portion of the ring is narrow, then there was not much rain that year. When aging a tree, just count either the light or the dark portion, not both. Leaves Leaf Function • Photosynthesis • Transpiration • Gas exchange • Monocots have parallel veins • Dicots have branched veins Dicot Monocot • • • • Stomata on the underside of leaves for gas exchange (CO2 & O2) Two guard cells on either side of the stomata open & close the openings When guard cells LOSE water, the stoma CLOSE, while the stoma OPEN when guard cells gain water & swell What time of day would the stoma be closed? Adaptations of Leaves Seeds • Seeds may be dormant (inactive) for weeks or years protected by their seed coat • Seeds contain a plant embryo and endosperm Dicot Seed Germination Seed Dispersal Water & Nutrient Transport • Vascular tissue conducts water & nutrients • The 2 types of vascular tissue are xylem & phloem • Xylem carries water and dissolved ions from the roots to stems and leaves • Phloem carries dissolved sugars from the leaves to all other parts of the plant Flowers • Flowers are the reproductive part of a plant. • Bright colors, attractive shapes, and fragrant aromas help flowering plants attract their pollinators (insects, birds, mammals...) Pollination • • • • • • • Wind, water, and animals help spread pollen As pollinators drink nectar or eat the fruit, pollen gets on their bodies and is spread to other flowers Self pollination occurs whenever pollen from a flower lands on the stigma of that SAME flower (pea plants) Cross pollination occurs whenever pollen is spread to a different flower producing hybrids When pollen lands on the stigma, a pollen tube grows through the style to the ovary Two sperm travel down the pollen tube --- one fertilizes the egg and the other join with polar nuclei to form endosperm (stored food for Seed) Called Double Fertilization Tropisms Gravitropism: gravity effect • Roots have +gravitropism • Stems have -gravitropism Phototropism: the sun effect • Phototropism causes a plant to grow toward a light source. Thigmotropism Carnivorous Plants • Some plants grow in environments that have low concentrations of nutrients in the soil. Specialized leaves trap and digest insects for nutrients.